-
Overview
-
Methods
-
Case Study
-
FAQs
-
Related Resources
-
Related Services
Overview
Solution instability occurs frequently, which leads to mismatching structure-activity relationship (SAR) of the compound and reducing its in vivo efficiency. An early understanding of stability deficiencies in a lead compound is valuable in the drug discovery stage. From a physiological point of view, the stability of a drug is affected by the environment in the body, especially the pH of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, the stability of a drug in different pH environments is very important. During the in vivo process, the compound should be stable enough to ensure it not be degraded in the gastrointestinal system, so that it has enough time to pass through the gastrointestinal tract into the blood circulation and eventually bring about ideal bioavailability. Solution stability is usually done in the early exploration phase, which helps prioritize different compound families in later phases, as well as alerting the researchers for potential problems in late phases. WuXi AppTec DMPK offers methods for the stability of compounds in aqueous buffer, simulated bio-relevant media, or other test media.
Learn More



Methods
-
Theoretical Concentration
2 μM or other specified concentration
Media
Aqueous buffer, bio-relevant media, biological assay buffers, organic solvents
Percentage of DMSO
1%
Incubation Equilibration Time
0, 1, 2, 6, 24 hours (or other time points)
Equilibration Temperature
Room temperature or 37 ℃
Sample Volume Required
30 μL of 10 mM DMSO stock solution
Analytical Method
LC-MS/MS
Turnaround Time
5 working days
Case Study
-
-

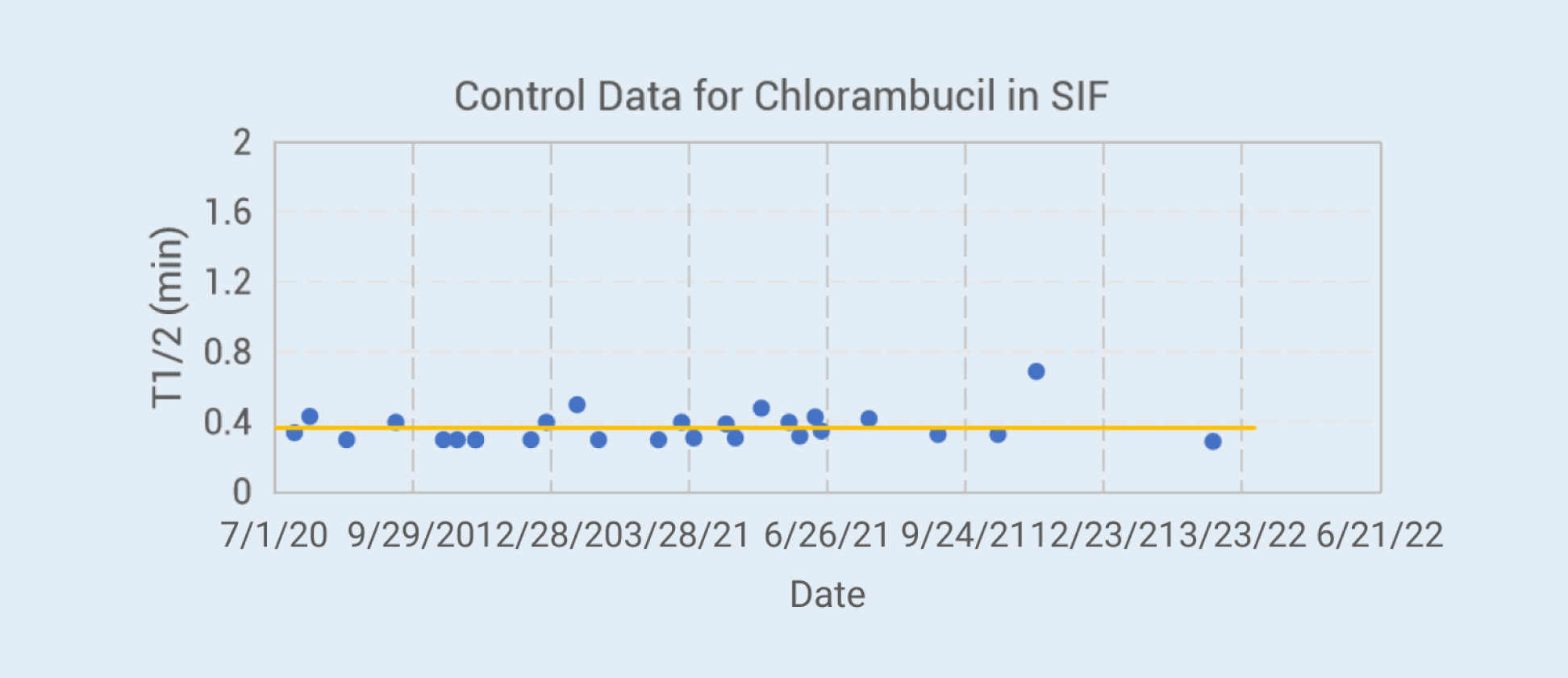
Control Data for Chlorambucil in SIF
WuXi AppTec DMPK has developed a method to evaluate the stability of compounds in aqueous buffers of different pH and simulated bio-relevant media, which has the advantages of convenient operation and accurate data. Part of the verification data for some commercial reagents are shown on the left.
-
FAQs
-
Why choose 75 mM phosphate buffer for the stability test?
The main purpose of the stability test of the compound in the aqueous buffers is to determine the changing trend of the compound at different pH. The phosphate buffer has a wide range of adjustable pH and is easy to operate, so the phosphate buffer is finally selected. Since the ionic strength affects the reaction rate, its concentration should be kept constant, thus 75 mM phosphate buffer with sufficient buffering capacity is finally chosen.
-
Why is the incubation concentration set to 2 μM?
The conditions for stability testing should ensure that the compound is completely dissolved in the solution for stability determination, usually by using a co-solvent or reducing the concentration of the test compound. Most compounds are not affected by solubility problems at 2 μM, so an incubation concentration of 2 μM is chosen.
-
What are the commonly used bio-relevant media for stability experiments?
The bio-relevant media include Simulated Gastric Fluid (SGF), Simulated Intestinal Fluid (SIF), Fed State Simulated Gastric Fluid (FeSSGF), Fed State Simulated Intestinal Fluid (FeSSIF), Fasted State Simulated Gastric Fluid (FaSSGF), Fasted State Simulated Intestinal Fluid (FaSSIF), etc.
-
How to ensure the accuracy of the measurement results?
The experiment is set with positive reference compound. And large amount of historical reference values have been collected to evaluate the accuracy of the experimental operation. In addition, a semi-quantitative method is used to measure the stability of the compound, and an internal standard is added to the stop solution to monitor the system stability of instrument. By measuring the values of parallel incubated two-well samples and calculating CV, the accuracy of response at each time point is fully ensured.
Related Resources




-


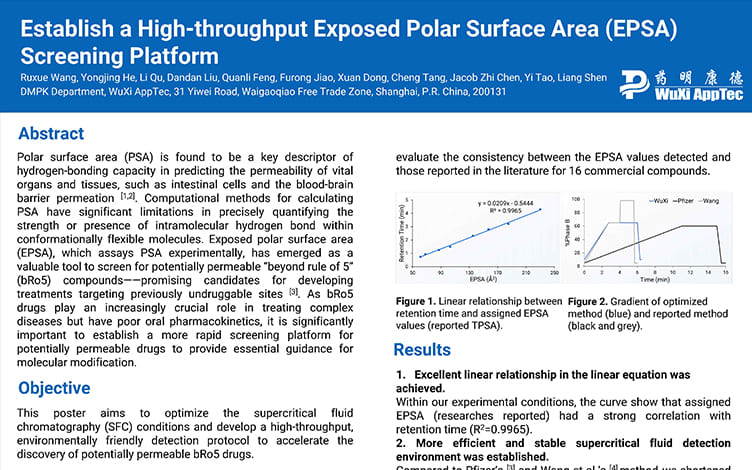
Establish a High-throughput Exposed Polar Surface Area (EPSA) Screening Platform
PostersSep 04, 2025Learn More -


Development of a High-throughput and Cost-effective Method for Experimental Polar Surface Area Measurement with Ultra-Performance Convergence Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
PostersJul 24, 2025Learn More -


Enhancing Permeability Through Exposed Polar Surface Area (EPSA) for Beyond Rule of Five (bRo5) Drug Candidates
ArticlesApr 10, 2025Learn More -


Rapid Determination of Lipophilicity: Exploration and Establishment of Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RPLC) Methods
PostersNov 05, 2024Learn More -


Ensuring drug product integrity: The crucial role of stability testing
BlogsOct 27, 2024Learn More -


How to Evaluate Lipophilicity Rapidly? The Significance of Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
BlogsDec 19, 2023Learn More -


Rapid Determination of Lipophilicity: Establishment and Application of Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
ArticlesNov 30, 2023Learn More -


Focusing on PROTAC Permeability and Solubility Improving the Oral Availability
BlogsJul 07, 2023Learn More -


Research on PROTAC Druggability: Solubility and Permeability
ArticlesJun 30, 2023Learn More
Stay Connected
Keep up with the latest news and insights.