-
Overview
-
Study Models and Platforms
-
Study Strategies and Assays
-
Case Study
-
FAQs
-
Related Resources
-
Related Services
Overview
WuXi AppTec DMPK has built a rational drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics (DMPK) research strategy for PDCs based on our experience by combining the principles and features of PDCs. We have accumulated extensive experience in in vitro ADME, in vivo pharmacokinetic, bioanalysis and metabolite identification studies. In addition, the research period could be significantly shortened by taking advantage of our strengths including the research strategies, data interpretation, etc.
Learn More


Study Models and Platforms
-
Payload release platform
There are four types of linkers for PDCs, including enzyme cleavable linker, GSH cleavable linker, acid cleavable linker and non-cleavable linker. According to the linker types of PDCs, selecting a suitable in vitro payload release model not only helps customize in vitro ADME assays, but also helps investigate the mechanism of action (MOA) of PDCs.

-
LC-MS/MS bioanalysis platform
The bioanalysis of PDCs may have matrix stability and non-specific binding (NSB) issues. In addition, it may encounter other problems, such as multiple charge states, low sensitivity, low extraction recovery, endogenous interference and so on. Due to the strong toxicity of payload, it is generally required to keep payload in tissues at very low level, which required the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of payload extremely low. WuXi AppTec DMPK has abundant and successful bioanalytical strategies to solve the existing issues of PDCs and has developed bioanalytical methods for common payloads with LLOQ at the level of pg/mL. In addition, we have accumulated rich experience in homogenizing various tissues, which helps to detect PDC and payload correctly by considering the matrix stability of PDCs.

-
Radioisotope platform
WuXi AppTec DMPK can carry out tissue distribution, metabolism, and excretion of PDCs in animals by using radioisotope labeling trace technology, or carry out tissue distribution in healthy or tumor-bearing animals by QWBA method. The 14C-labeled PDCs can be synthesized in WuXi AppTec DMPK, and a reasonable labeling site can be designed according to the chemical structure, synthesis process, and metabolite identification results.

Study Strategies and Assays
-
In screening stage, the main content of DMPK research is to investigate the stability of homing peptide and PDC in whole blood, plasma, and kidney homogenate. The structure of PDC is further optimized through in vitro and in vivo MID. According to the different types of linkers (non-cleavable or cleavable; if cleavable, refer to cleavage mode), a suitable in vitro model is selected to evaluate the release of payload. It is suggested to study the tissue distribution of rodents in the early stage to evaluate the potential toxicity of payload in different organs.
In preclinical candidate (PCC) stage, a suitable in vitro model is recommended to evaluate the release of payload and the metabolism of PDC. It is necessary to simultaneously detect concentration of PDC and payload in plasma. In the case of repeated administration, it is recommended to monitor anti-drug antibodies. Tissue distribution study could be performed in pharmacodynamics (PD)-relevant species to evaluate the targeting of PDC.
In IND-enabling stage, if the payload is brand-new, a comprehensive in vitro evaluation of the payload is needed. It is suggested radiolabeled PDC is used to study the tissue distribution and mass balance in rodents.
Screening | PCC | IND-enabling | |
In vitro | In vitro metabolic stability and MID of homing peptide and PDC in whole blood, plasma and liver or kidney homogenate (or S9) Stability of PDC in cathepsin (or lysosome, or buffer at different pH, or Glutathione) (depending on the type of linker) Blood/plasma ratio of payload PPB and tissue protein binding of PDC and payload | MID in tumor cells | PPB for PDC Stability in plasma, liver or kidney homogenate of PDC and the corresponding MID studies for PDC CYP inhibition, induction and transport inhibition for PDC In vitro ADME studies for payload |
In vivo | MID of peptide and PDC in plasma and urine from in vivo studies. PK of peptide PK and tissue distribution of PDC | Non-rodent PK of PDC Tissue distribution of PDC in PD models | Bio-analytical method qualification for PDC and payload Dose linearity of PDC In vivo MID for PDC Tissue distribution and mass balance of PDC |
Case Study
-
-

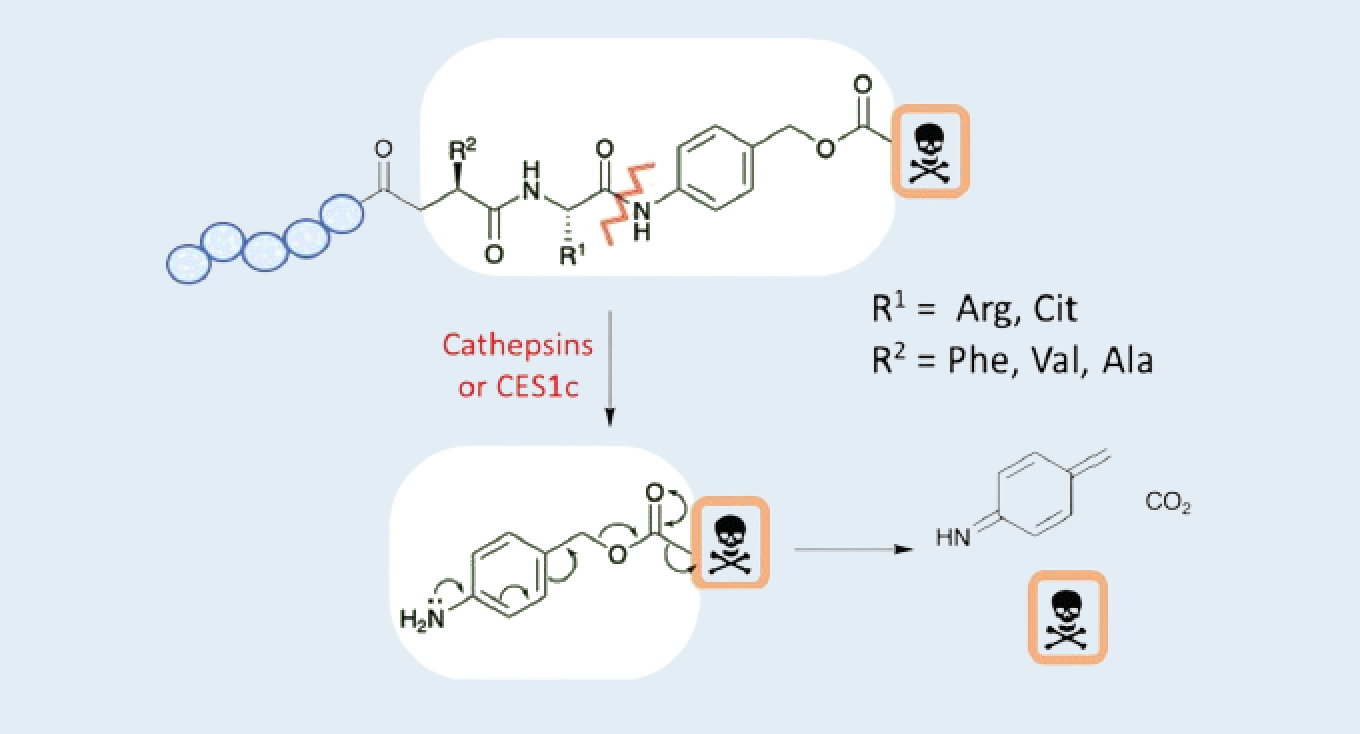
Customized design: The homing peptide was linked to p-aminobenzyl carbamate (PABC) and MMAE via Val-Cit dipeptides. To our knowledge, the CES1c enzyme from mouse plasma probably hydrolyze this linker to release MMAE. If mouse plasma was directly collected without stability tests, the detected concentrations of MMAE and PDC may be unreliable. Because the release of MMAE hydrolyzed by CES1c enzyme from mouse plasma will increase the concentration of MMAE while the concentration of PDC will decrease during plasma sample processing. Therefore, we developed the bioanalytical method and investigate the matrix stability first. Based on bioanalytical method and matrix stability result, direct protein precipitation in the plasma afforded the supernatant immediately after collection to avoid freeze-thaw stability of PDC in the matrix, and specific absorption inhibitor Triton X-100 was added to remove non-specific binding.
Test results: Reliable bioanalysis results were obtained after following our suggestion. During the bioanalysis of PDC samples, special attention should be given to the issues such as stability and non-specific binding.
Learn More
-
FAQs
-
What is PDC?
PDC (Peptide-Drug Conjugate) is a coupling drug by using homing peptide as the targeting molecule, which consists of homing peptide, linker, and payload. By taking advantage of homing peptide's high affinity with the receptors on tumor surface, PDCs deliver payloads to tumor cells and kill them through intracellular or extracellular release of payloads.
-
What are the advantages and disadvantages of PDC compared with ADC?
Advantages: compared with ADCs, PDCs have smaller molecular weight, and are featured for better tissue penetration and no or low immunogenicity; In addition, the CMC of PDCs is much easier than that of ADCs at a cheaper price.
Disadvantages: The antibody of ADC is more stable than peptide in PDC, and stability is not an issue for ADC. In addition, the targeting of homing peptides is not superior to antibodies.
-
What are the typical problems of PDCs may have in DMPK studies?
PDCs may face some bioanalytical problems such as multi-charge state, low sensitivity, low extraction recovery, and endogenous interference. As a new modality, PDCs are composed of three components. At present, there is no guidance from regulatory agency or a consensus on the assays to be carried out for each component.
-
What diseases are treated with PDC?
Researchers are actively developing new PDC therapies for various cancers, including glioblastoma, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, and other solid tumors, with several candidates currently in clinical trials showing promising results for targeted cancer treatment. With the good targeting of peptides, PDC also shows potential in other disease areas, such as CNS, etc.
Related Resources




-


Peptide-Radionuclide Conjugates: Interpretation of FDA Approved Drugs and DMPK Strategies
ArticlesJun 06, 2024Learn More -


The Importance of Drug Conjugate Linker Design: Effect on the Pharmacokinetic (PK), Drug Efficacy, and Toxicity Profiles
BlogsAug 18, 2023Learn More -


Drug Conjugate Linkers and Their Effects on Drug Properties
ArticlesAug 10, 2023Learn More -


Preclinical Drug Development Testing for Peptide-Drug Conjugate (PDC)
BrochuresMay 11, 2023Learn More
Stay Connected
Keep up with the latest news and insights.