-
Overview
-
Assays
-
Animal Species
-
Routes of Administration
-
Surgical Models
-
Experience
-
Facilities
-
FAQs
-
Related Resources
-
Related Services
Overview
Since 2007, WuXi AppTec DMPK has been providing exceptional large animal testing services for drug metabolism to global drug development institutions. With different kinds of species including monkeys, dogs, pigs, rabbits, and ferrets, we are ready to meet diverse experimental needs. Our digital and intelligent work mode, combined with advanced equipment and smart data management, ensures real-time monitoring, accuracy, and reliability of data. Our experienced scientists provide insightful analysis and effective solutions. We always prioritize customer satisfaction, rigorous scientific approach, and precise operations. Through our innovative services, we aim to enhance drug development efficiency and speed up the market launch. Let’s collaborate to advance drug development and contribute to human health.
Learn More


Assays
-
Hit to lead
Fast PK:
Large animal PK (oral or intravenous administration),single or cassette administration
-
Lead optimization
PK study in large animals (administered through oral, intravenous, short term infusion or 72-hour ambulatory infusion pump, subcutaneous, intramuscular, and Intrathecal routes.
Single or multiple doses
Exposure studies with different formulation
-
Preclinical candidate (PCC)
Single-dose or multiple-dose study following specific administration route
PK studies with different salt forms or crystal forms
PK studies with different dosage forms (Tablet, capsule, SDD, Nano-suspension, SEDDS), including bridging studies with clinical formulations
Food effect studies (high-fat food, maintenance food)
PK studies with adjustment the gastric pH (pentagastrin, famotidine)
Maximum tolerated dose experiment (MTD) and dose escalation experiment
-
Investigational New Drug (IND) application
PK studies of single-dose and single intravenous administration
Oral administration PK studies with high, medium, and low doses
PK studies of medium dose and multiple oral administration
Tissue distribution studies after a single oral administration
Biliary excretion studies with medium dose and single oral administration
Urine and fecal excretion studies with medium dose and oral administration
Identify major metabolites in plasma and excretion
Animal Species
-
Dog
Beagle Dog
-
Monkey
Cynomolgus
Rhesus Macaques
Marmosets
-
Minipig
Bama Mini-pig
-
Rabbit
New Zealand White Rabbit
Chinchilla Rabbit
Dutch Rabbit
Japanese White Rabbit
-
Ferret
Sable Ferret
Routes of Administration
Drug administration is a vital component of in vivo PK studies. Proper administration route selection is of great significance during early drug screening and late drug development. A variety of administration routes have been developed according to client demand and forward-looking marketplace strategies to provide high-quality in vivo PK Study service for thousands of clients worldwide. Specialized and high-quality skills and techniques include, but are not limited to, single-dose administration, multiple-dose administration over consecutive days, continuous intravenous infusion for 72 hours without anesthesia, ocular administration, transdermal administration, intrathecal injection, etc. We constantly strive to provide better service and continuous improvement.
-
-
CNS
Intra-cerebroventricular dosing
Intrathecal dosing
-
Percutaneous drug delivery
Intradermal injection
Skin (Ointment, Patch, Gel, Films, Spray)
-
Infusion
Long-term intravenous injection
Hepatic portal vein injection
Intravenous bolus
-
Ophthalmic drug delivery
Intravitreous injection
Intracameral injection
Eyedrop dosing
-
Oral cavity
Sublingual dosing
Buccal patch
Sublingual patch
Orally disintegrating tablet
-
Enteral administration
Duodenal dosing
Jejunal dosing
Ileal dosing
Cecal dosing
Colonic dosing
Rectal dosing
-
System or site
Dose route
-
Intranasal (spray, drip)
-
Intra-articular injection
-
Intraperitoneal injection
-
Intravaginal dosing
-
Intraosseous dosing
-
Bladder dosing
-
-
Surgical Models
Case Sharing of Surgical Model
Large animal PK surgical models are important tools for pharmacokinetic research of drugs. Through setting up surgery models, complex drug administration or sample collection can be carried out, helping researchers to have a deeper understanding of the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs in the body. WuXi AppTec DMPK has professional surgical veterinarians with decades of experience in the development and operation of large animal surgical models, and can provide precise and reliable surgical model services, providing strong support for drug research and development.
-
-
Vascular cannula
Femoral vein cannulated
Hepatic portal vein cannula
A peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC)
-
Non-vascular cannula
Bile duct cannula
Intestinal cannula
Mesenteric lymph duct cannula
Cervical lymphatics cannula
Thoracic duct cannula
Cisterna magna cannula
-
Special operations
Whole-body tissue perfusion
Nasal mucosal lavage
Bronchoalveolar lavage
Intraarticular puncture
Bone marrow aspiration
CSF puncture
-
Biopsy
Liver Biopsy
Skin Biopsy
Muscle Biopsy
Kidney Biopsy
-
-
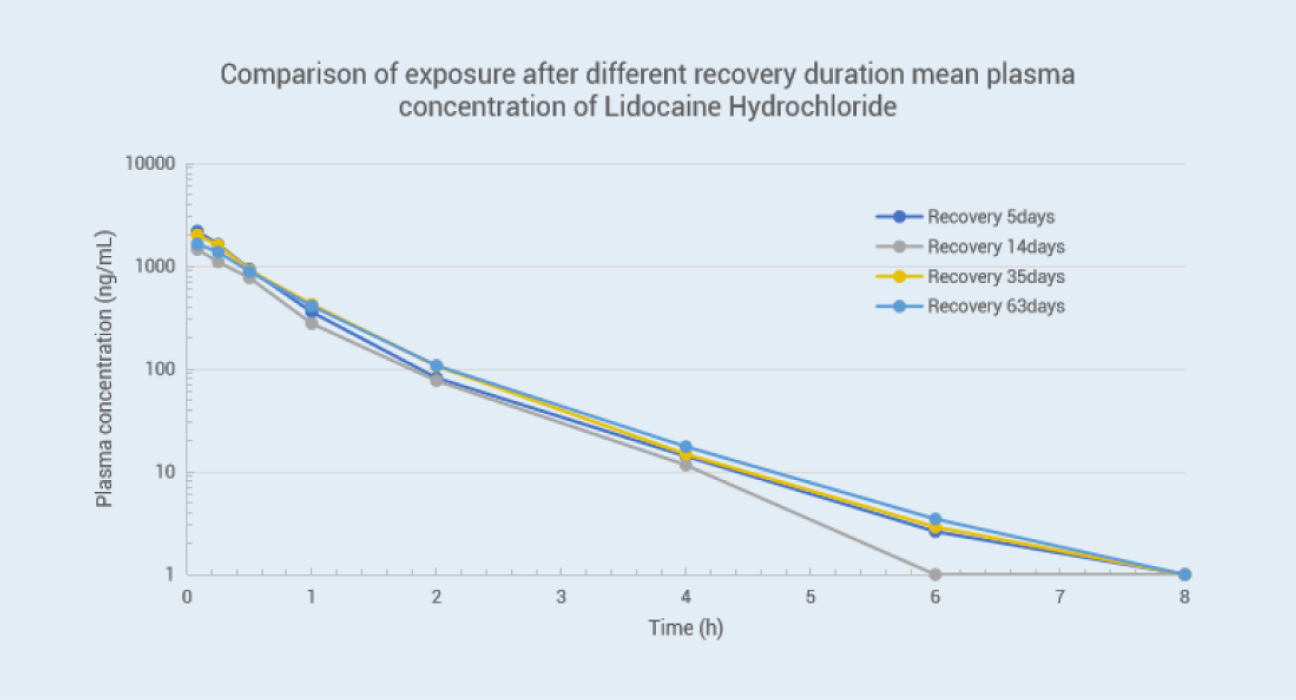
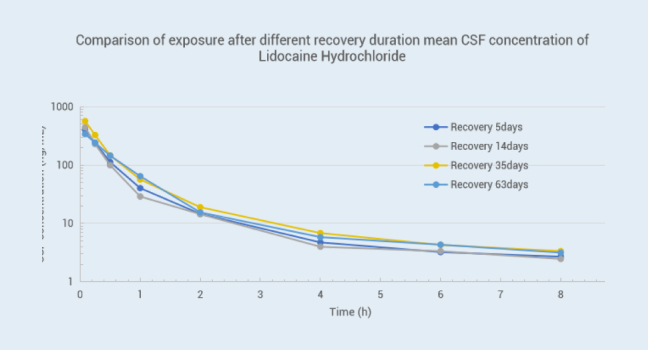
For drugs acting directly on the central nervous system, accurate detection of drug concentration in the brain contributes to evaluate the ability of drugs towards the target site. Moreover, the direct measurement of drug concentration of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) has more accuracy than using the concentration of free drug in plasma to predict the drug concentration in the brain 1, 2. The drug concentration of CSF can be used as an effective indicator for evaluating drug exposure for those CNS (Central Nervous System) drugs and provide a basis for these drug candidates to move to the next stage. We have established Cisterna Magna cannulation (CMC) models in monkeys and canines according to the literature 3 since 2009, which allows us to collect CSF samples consecutively without anesthesia to obtain relevant PK curves and evaluate the drug's ability to cross the BBB (blood-brain barrier). The longest patency of catheter in CMC model animal was up to 2 years, and we have standby CMC model animals for use anytime to shorten the leading time. Nearly 500 projects, including IND applications, were completed by 2023.
Objective: To compare the stability of the CMC model in dogs with different surgery recovery times.
METHODS: Lidocaine hydrochloride injection drug (25 mg/dog) was administered intravenously in 3 male beagle dogs five days, 14 days, 35 days, and 63 days after surgery. The plasma and CSF samples were collected at the same time point, and the results of drug concentration were as follows:Conclusion: The data showed a slight deviation in drug concentration between the plasma and CSF matrix on postoperative days 5, 14, 35, and 63, indicating that our animal surgical model is reliable with consistent data.
Learn More
-
List of biological sample collection of large animals
Whole blood
Plasma
Serum
White blood cell
Erythrocytes
PBMC
Stratum corneum
Epidermis
Dermis
Subcutaneous tissue
Ocular tissues*
Brain tissue**
Bone marrow
Organs
Intestinal fluid
Gastric fluid
Joint fluid
Rectal mucosa
Oral mucosa
Nasal mucosa
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (multiple consecutive)
Lymph (surgical)
Bile (surgical)
Urine (metabolic cage)
Urine (puncture)
Urine (Cannula)
Feces (metabolic cage)
Biopsy of skin, muscle, liver tissue
The samples of ocular tissues include but are not limited to conjunctiva, cornea, iris, lens, ciliary body, retina, choroid, sclera, optic nerve, aqueous humor, vitreous body, and tear.
Samples of various brain tissues include but are not limited to the caudate nucleus, cerebellum, cerebral cortex, white matter of the cerebrum, cingulate gyrus, cingulate sulcus, corpus callosum, external capsule, internal capsule, globus pallidus, hippocampus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, midbrain, medulla oblongata, optic nerve, optic chiasm, pons, shell, and spinal cord.
Experience
-
17+
Years of experience
-
100+/Year
Lager animal IND
-
20000+m2
Large animal facility
-
3,000+
Colony animals
Facilities
In-house AAALAC accredited animal facilities to house monkey, Dog, Mini-pig, Rabbit, Ferret
-


AAALAC Certificate
-
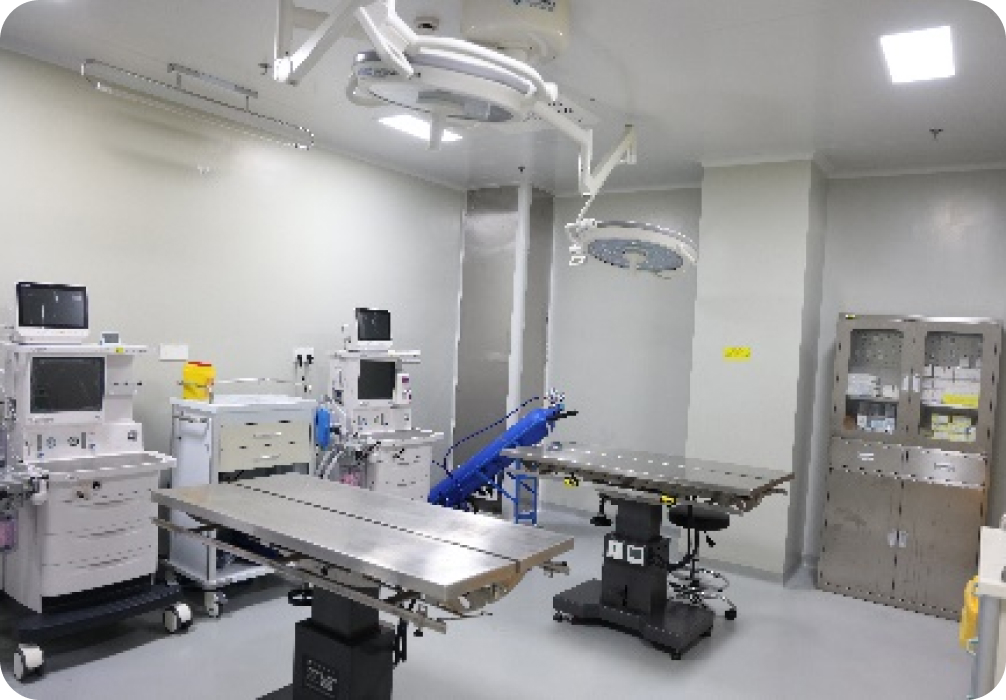


Surgery Room
-


Fruit Storage Room
-


Corridor
-


Cage Washer Room
-
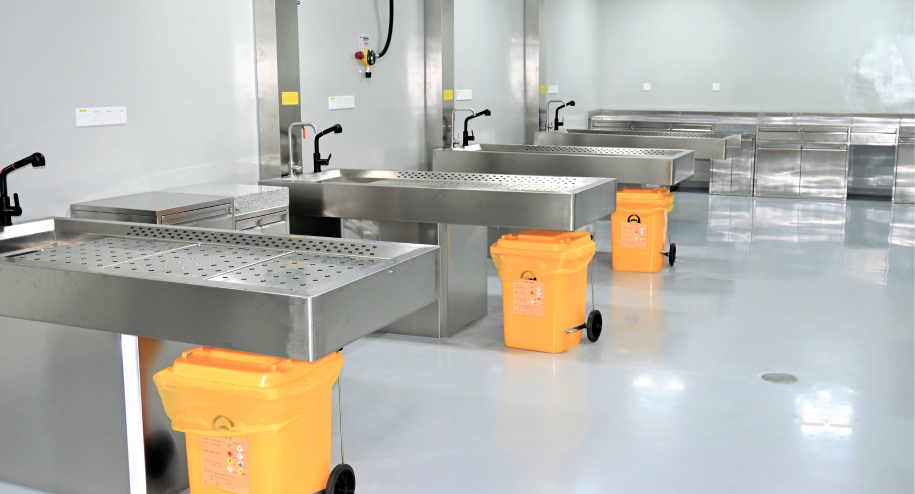


Necropsy Room
-


Feed Storage Room
-


EU Dog Exercise Area
-


Mini-pig Exercise Area
-


EU Monkey Cage
Learn more about our facilities
Including mouse,rat,hamster,monkey,dog,pig,rabbit,etc
FAQs
-
What are large animals (non-rodent animals) PK studies?
Pharmacokinetic (PK) studies in large animals (non-rodent animals) involve the examination of the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs within these animals. The purpose is mainly for dose optimization and predicting human pharmacokinetics.A Large Animal PK (Pharmacokinetic) study refers to the study of how a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted in large animals (non-rodent animals).
-
What is the significance of large animal PK?
Predicting Human Pharmacokinetics: Large animals often share physiological similarities with humans, making them valuable for predicting human drug behavior.
Safety and Efficacy Assessment: Understanding the PK profile helps in assessing the safety and efficacy of drugs before human trials.
Dose Optimization: Determining appropriate dosing regimens by studying drug dynamics in a larger biological system.
Regulatory Compliance: Meeting the requirements of regulatory agencies for drug approval processes.
Common large animals used in these studies include dogs, non-human primates, pigs, and occasionally sheep. The choice of species depends on the specific goals of the study, ethical considerations, and the relevance to human physiology.
-
What large animals are used in preclinical trials?
In preclinical (PK)studies, large animals are selected based on their physiological, anatomical, metabolic enzyme profiles, or genetic similarities to humans, as well as their suitability for specific research applications. The primary large animals used in PK studies include non-human primates (such as monkeys), dogs, pigs, and rabbits. Occasionally, other animals such as fishes, cats, ferrets, or sheep may also be used in specific contexts.
-
Why are large animals (non-rodent animals) used in pharmacokinetic research?
Large animals (non-rodent animals) are used in pharmacokinetic research for several scientifically substantiated reasons:
Physiological Relevance: Large animals often have physiological and anatomical characteristics that are more comparable to humans than those of rodents, allowing for more accurate extrapolation of pharmacokinetic data to human scenarios.
Metabolic Similarities: The metabolic pathways in large animals can closely resemble those in humans, providing more predictive insights into drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME).
Dosing and Scaling: The larger body size of these animals permits the investigation of drug dosages and administration volumes that are relevant to human therapeutic use, facilitating more accurate dose scaling.
Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory agencies frequently require pharmacokinetic data from non-rodent species to ensure the safety and efficacy of new drugs before they are approved for human clinical trials.
Modeling Complex Diseases: Large animals can serve as valuable models for studying chronic or complex diseases that are difficult to replicate in smaller animals, leading to more relevant pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data.
By providing a more accurate reflection of human responses, the use of large animals in pharmacokinetic research is essential for the development and regulatory approval of new pharmaceuticals.
Related Resources




-


Liposome Drug Delivery: Classification, Composition, and Formulation Considerations
ArticlesJan 16, 2026Learn More -


The Role of Lymphatic Transport on the Systemic Bioavailability of the Bcl-2 Protein Family Inhibitors Navitoclax (ABT-263) and ABT-199
PublicationsJan 16, 2026Learn More -


Development and Implementation of a Ferret Venous Catheterization Model for Pharmacokinetic Studies
PostersNov 28, 2025Learn More -


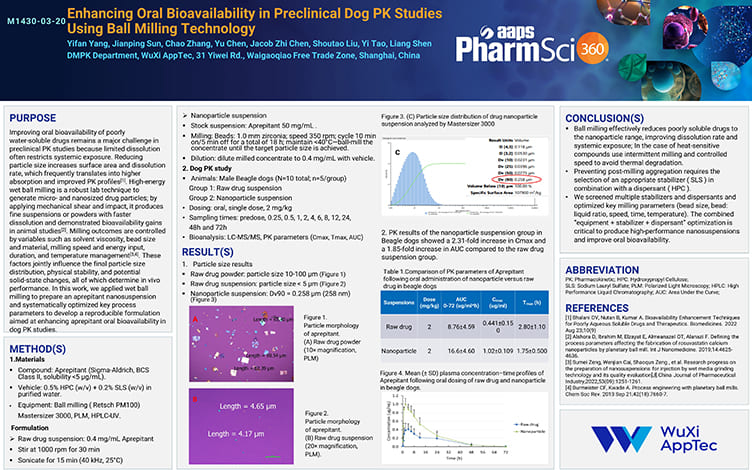
Enhancing Oral Bioavailability in Preclinical Dog PK Studies Using Ball Milling Technology
PostersNov 28, 2025Learn More -


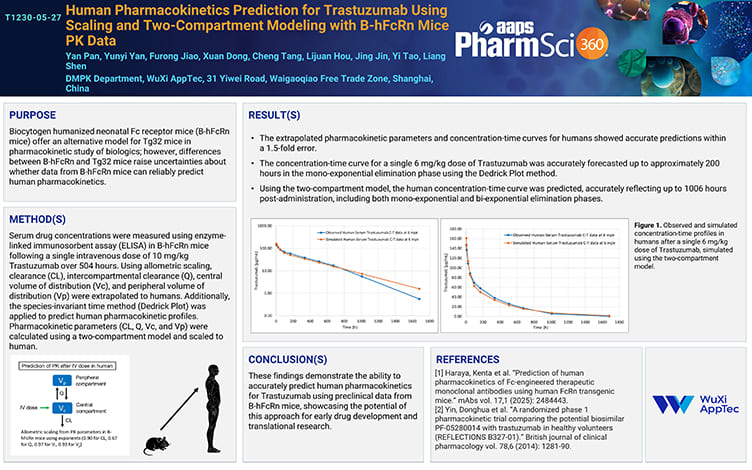
Human Pharmacokinetics Prediction for Trastuzumab Using Scaling and Two-Compartment Modeling with B-hFcRn Mice PK Data
PostersOct 11, 2025Learn More -


What Is Brain Microdialysis and Its Application in PK Studies for CNS Drugs
ArticlesSep 26, 2025Learn More -


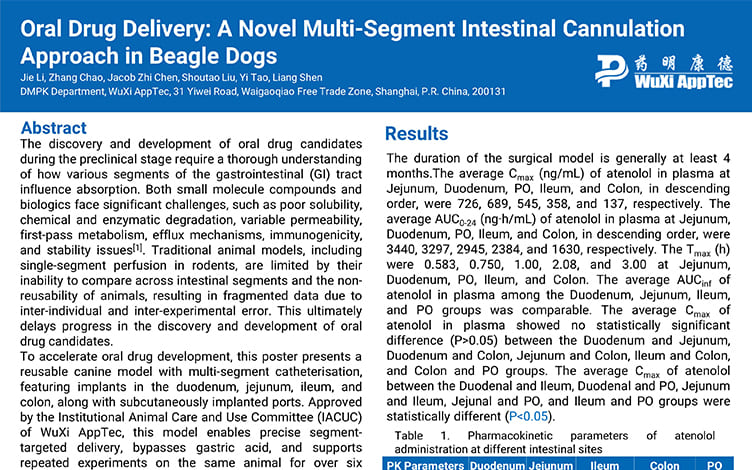
Oral Drug Delivery: A Novel Multi-Segment Intestinal Cannulation Approach in Beagle Dogs
PostersSep 19, 2025Learn More -


Factsheet-Intrathecal Administration in Rats and Monkeys
BrochuresAug 08, 2025Learn More -


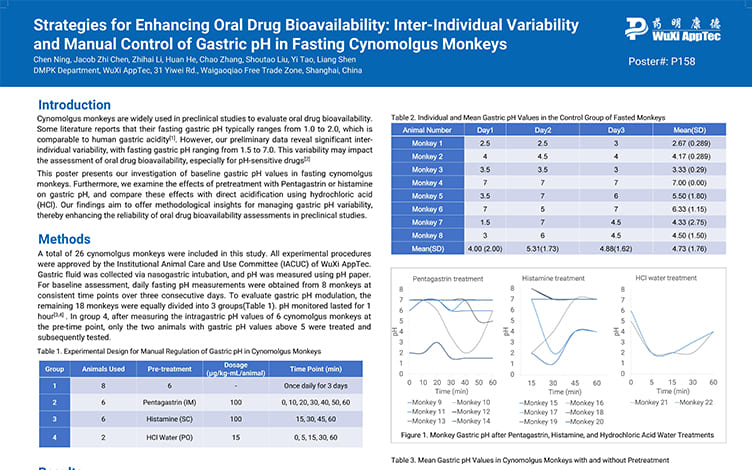
Strategies for Enhancing Oral Drug Bioavailability: Inter-Individual Variability and Manual Control of Gastric pH in Fasting Cynomolgus Monkeys
PostersJun 20, 2025Learn More -


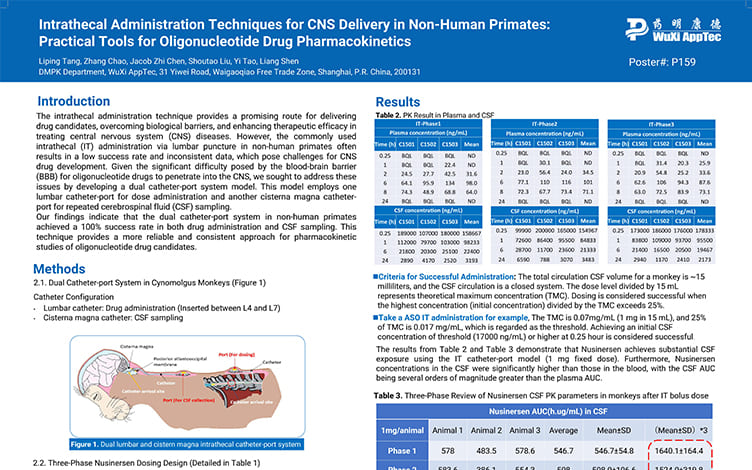
Intrathecal Administration Techniques for CNS Delivery in Non-Human Primates:Practical Tools for Oligonucleotide Drug Pharmacokinetics
PostersJun 05, 2025Learn More -


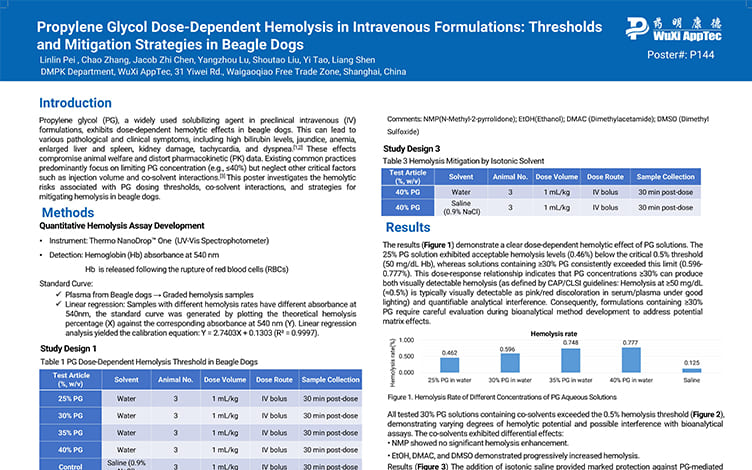
Propylene Glycol Dose-Dependent Hemolysis in Intravenous Formulations: Thresholds and Mitigation Strategies in Beagle Dogs
PostersJun 05, 2025Learn More -


Advancements in Pet Drugs and Pharmacokinetic Insights from FDA-Approved Products
ArticlesFeb 06, 2025Learn More -


Application and Best Practices of Liver Biopsy in Non-Rodents
BlogsNov 28, 2024Learn More -


4 Best Practices for Intrathecal Administration in CNS Drug Development
BlogsNov 12, 2024Learn More -


In Vivo PK | What Are We Striving For?
VideosOct 17, 2024Learn More -


Evaluation of Different Tissue Processing Methods in Bama Pig Skin as an Animal Model for Topical Delivery Systems
PostersSep 19, 2024Learn More -


Application of Innovative Intelligent Electronic Cage Cards in Large-Scale Animal Facilities
PostersAug 25, 2024Learn More -


Large Animal (Non-Rodent) PK Study Part Ⅲ List of Organ and Tissue Collection
BrochuresAug 21, 2024Learn More -


Large Animal (Non-Rodent) PK Study Part Ⅱ Surgical Models
BrochuresAug 21, 2024Learn More -


Large Animal (Non-Rodent) PK Study Part Ⅰ Route of Administration
BrochuresAug 21, 2024Learn More -


Intrathecal Antisense Oligonucleotides: PK and Strategy
ArticlesJul 04, 2024Learn More -


Transdermal Drug Delivery System (TDDS): Research Overview and Methods for Enhancing Skin Permeability
BlogsMar 29, 2024Learn More -


Evaluating In Vivo Pharmacokinetics for Transdermal Drugs Strategies and Methods
ArticlesMar 21, 2024Learn More -


In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Service
BrochuresJun 21, 2023Learn More
References
- 1.
Maurer TS, DeBartolo DB, Tess DA, Scott DO (2005) Relationship between exposure and non-specific thirty-binding of three central nervous system drugs in mice. Drug Metab Dispos 33:175-181
- 2.
Liu X, et al. (2009) Unbound drug concentration in brain homogenate and cerebral spinal fluid at steady state as a surrogate for unbound concentration in brain interstitial fluid. Drug Metab Dispos 37:787-793
- 3.
Gilberto DB, Zeoli AH, Szczerba PJ, Gehret JR, Holahan MA, Sitko GR, Johnson CA, Cook JJ, Motzel SL. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci. 2003 Jul; 42 (4): 53-9
Stay Connected
Keep up with the latest news and insights.