-
Overview
-
Assays
-
Case Study
-
Regulatory Guidance
-
Experience
-
Instruments and Software
-
FAQs
-
Related Resources
-
Related Services
Overview
The in vivo MetID platform at WuXi AppTec DMPK offers three types of metabolic studies for different experimental purposes: circulation and excreta metabolism study in animals, and clinical metabolism study. In addition, the established in vivo MetID platform has performed metabolite profiling and identification of lead compounds and drug candidates with a variety of structures, including conventional small molecules, high-polar and non-polar small molecules, natural products, nucleotides, Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras (PROTACs*), polysaccharides, peptides, ADCs, PDCs, oligonucleotides, etc. Sample matrices include whole blood, plasma, urine, feces, bile, tissues, etc.
Learn More


Assays
Case Study
-
-

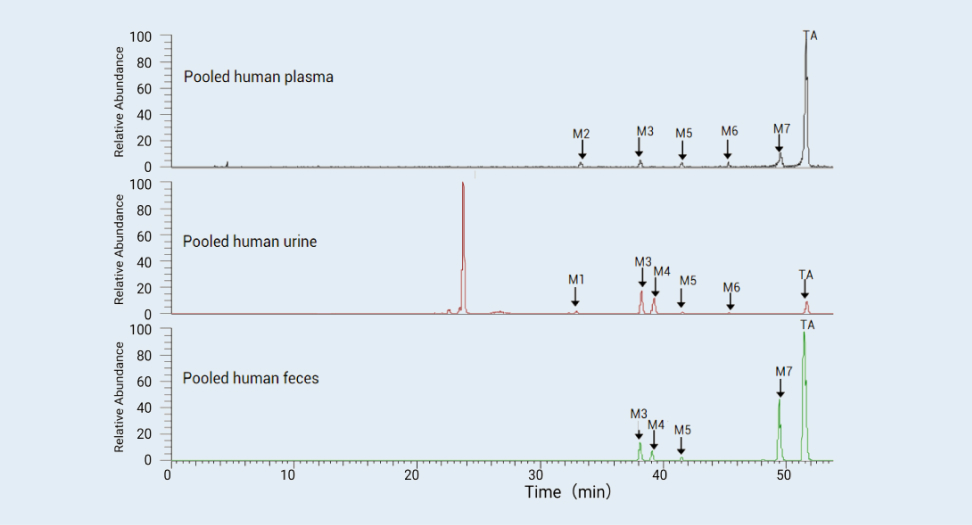
Metabolite profiles in plasma, urine, and feces of human
Figure1
Result: Figure 1 are metabolite profiling and ID results of pooled human plasma, urine and feces using LC/HRMS. The results indicate that the parent drug is the major pharmacological component exposed, while multiple minor metabolites are present in plasma. Metabolite M3 and M4 (glucuronidation) and M7 (mono-oxygenation metabolite) are most likely the major metabolites in urine and feces, suggesting that the formation of M3/M4 and M7 may be major metabolic clearance pathways in human. Several minor metabolic pathways lead to minor metabolites in urine and feces. The parent drug is a major drug-related component in feces, which may be unabsorbed, excreted into bile and/or from hydrolysis of M3 and M4 and other glucuronides in feces. The parent drug is a minor drug-related component in urine, suggesting that direct excretion of the parent drug from kidney to urine is not a major clearance pathway.
-
Experience
-
16+
Years of experience
-
500+
Submissions of IND applications
-
2000+
Screening projects
Instruments and Software
-
-


Thermo Orbitrap Eclipse™ Tribrid™
-


Thermo Orbitrap Exploris™ 480
-


Thermo Q-Exactive™ HF
-


Waters VION™ IMS QTof
-


Thermo Q-Exactive™ Plus
-


Thermo Q-Exactive™
-


Therno LTQ Orbitrap XL
-


Waters Xevo®G2 QTof
-


Solid scintillation counter: off-line detection of radioactivity
-


Liquid scintillation counter: total radioactivity detection
-


On-line detection of radioactivity
-
-
-


Thermo Scientific™ Compound Discoverer™
-


Thermo Scientific™ Mass Frontier™
-


Thermo Scientific™ Metworks™
-


Waters MetaboLynxTM
-


Mass Analytical Mass-MetaSite
-


Waters UNIFI®
-


Thermo Scientific™ Biopharma Finder™
-
FAQs
Related Resources




-


A Review on ADC Linkers: Cleavable and Non-Cleavable Linker Design and Stability Evaluation
ArticlesJan 30, 2026Learn More -


Software-aided Detection and Structural Characterization of Cyclic Peptide Metabolites in Biological Matrix by High-resolution Mass Spectrometry
PublicationsJan 09, 2026Learn More -


Practical Derivatization Approaches for LC‑HRMS Metabolite Profiling
ArticlesDec 30, 2025Learn More -


High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry-Based Data Acquisition and Data-Mining Technologies for Detecting and Characterizing Drug Metabolites and Traditional Chinese Medicine Components
PublicationsDec 11, 2025Learn More -


What Are Antibody–Oligonucleotide Conjugates (AOCs) and Their Structural Characteristics
ArticlesNov 28, 2025Learn More -


Overcoming Challenges in Oligonucleotide Metabolism with Innovative Solutions -WuXi AppTec DMPK TechTalk
VideosNov 07, 2025Learn More -


Rapid Screening and Characterization of Payload-Related Catabolites Derived from ADCs in In Vitro Models by UPLC-UV-HRMS
PostersOct 22, 2025Learn More -


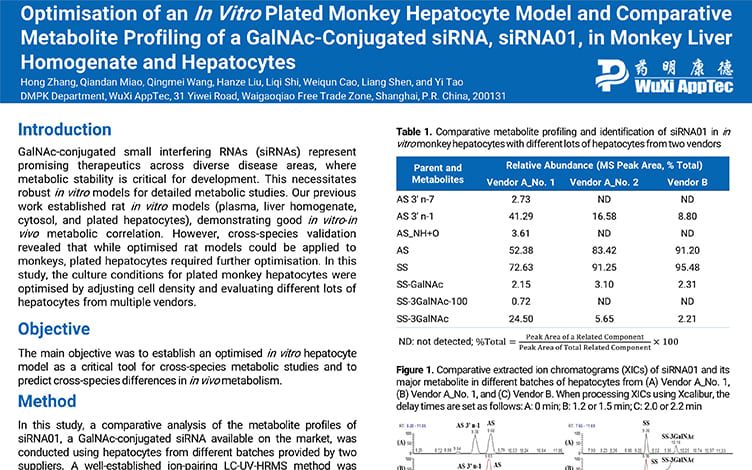
Optimisation of an In Vitro Plated Monkey Hepatocyte Model and Comparative Metabolite Profiling of a GalNAc-Conjugated siRNA, siRNA01, in Monkey Liver Homogenate and Hepatocytes
PostersSep 26, 2025Learn More -


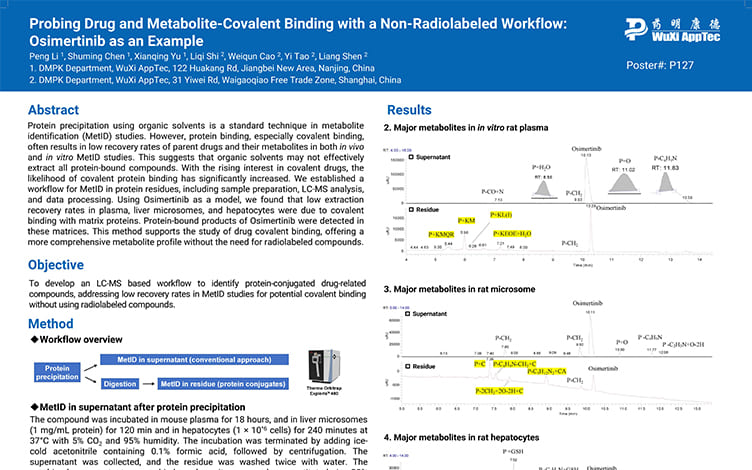
Probing Drug and Metabolite-Covalent Binding with a Non-Radiolabeled Workflow: Osimertinib as an Example
PostersAug 15, 2025Learn More -


Precision Metabolite Identification & Biotransformation for Drug R&D-WuXi AppTec DMPK
VideosJul 24, 2025Learn More -


New Book Release: Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics: Frontiers, Strategies, and Applications | WuXi AppTec DMPK
VideosJul 17, 2025Learn More -


Decoding DMPK Frontiers for Novel Therapeutics: WuXi AppTec DMPK’s New Book Release
BlogsJul 10, 2025Learn More -


Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics: Frontiers, Strategies, and Applications
PublicationsJun 13, 2025Learn More -


Unlocking Reliable In Vitro Metabolic Models for Oligonucleotide Therapeutics with the Latest Publication on DMD
BlogsMay 28, 2025Learn More -


High-Performance, Professional, Innovative: WuXi AppTec DMPK Accelerates Breakthroughs
VideosMay 22, 2025Learn More -


Comparative Metabolism of a GalNAc-Conjugated siRNA, Inclisiran, Among Various In Vitro Systems and Correlations with In Vivo Metabolism in Rats
PublicationsMay 08, 2025Learn More -


Detection and Characterization of In Vitro Payload-Containing Catabolites of Noncleavable Antibody-Drug Conjugates by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Multiple Data Mining Tools
PublicationsApr 28, 2025Learn More -


Covalent Drugs DMPK Services
BrochuresApr 10, 2025Learn More -


Unlocking Precision in Peptide Metabolite Identification for Next-Gen Drug Development
ArticlesMar 19, 2025Learn More -


Insights into Chiral Drug Metabolism and Inversion
ArticlesFeb 13, 2025Learn More -


Methodologies and Strategies for ADC Biotransformation Studies
WebinarsJan 15, 2025Learn More -


WuXi AppTec DMPK: Your Trustworthy Partner
VideosDec 27, 2024Learn More -


Metabolite Identification in Peptide Drugs and Its Challenges
ArticlesDec 02, 2024Learn More -


Comparative Metabolite Profiling and Identification of a GalNAc-Conjugated siRNA, siRNA01, in Plasma Prepared with Various Anticoagulants, Serum, and In Vivo Plasma Using LC-UV-HRMS
PostersOct 25, 2024Learn More -


Overcoming Challenges in Precise Structural Identification of Target Metabolites
WebinarsOct 12, 2024Learn More -


Involvement of Aldehyde Oxidase (AOXs) in Drug Metabolism: Early Prediction and Coping Strategies
ArticlesSep 26, 2024Learn More -


Prodrug Approaches for Improved DMPK Characteristics and Their Preclinical Study Considerations
ArticlesAug 29, 2024Learn More -


An Analytical Workflow for Polymer Metabolism: PEGylated Lipids Biotransformation with LC-HRMS
PostersJun 27, 2024Learn More -


Development of a Convenient In Vitro Method for Predicting Metabolism and Disposition of Acrylamide Covalent Drugs in Humans
PostersMar 21, 2024Learn More -


Effect of pH on Metabolite Profiling and Identification of GalNAc Conjugated siRNA in In Vitro Metabolic System
PostersJan 23, 2024Learn More -


Metabolite Profiling and Identification of Oligonucleotide in In Vitro Metabolic System
PostersOct 30, 2023Learn More -


DAR Distribution Determination for Antibody-drug-conjugates (ADCs) by LC-HRMS in In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
PostersOct 27, 2023Learn More -


Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (DMPK) Service
BrochuresOct 27, 2023Learn More -


One-stop Metabolite Biosynthesis and Structural Characterization
BrochuresOct 27, 2023Learn More -


Overcoming the Challenges of Metabolite Identification and Profiling for Developing Oligonucleotides
BlogsOct 20, 2023Learn More -


Metabolite Profiling & Identification (MetID) Services
BrochuresOct 19, 2023Learn More -


Oligonucleotide Drugs: Strategies for Metabolism and Metabolite Profiling and Identification
ArticlesSep 13, 2023Learn More -


In Vitro-In Vivo Metabolite Profiling and Identification of Oligonucleotide
PostersAug 30, 2023Learn More -


A New Method to Improve Identification of the Payload-Containing Catabolites of ADCs
BlogsAug 10, 2023Learn More -


How to Address the Challenges of PROTAC Metabolism
BlogsJul 13, 2023Learn More -


How MetID Studies can Improve Safety and Efficacy in PROTAC Drugs
ArticlesJul 07, 2023Learn More
Reference
- 1.
C. E. Hop, Z. Wang, Q. Chen, G. Kwei, Plasma-Pooling Methods to Increase Throughput for in vivo Pharmacokinetic Screening, J. Pharm. Sci., 87 (1998) 901-903.
Stay Connected
Keep up with the latest news and insights.