-
Overview
-
Assays
-
Case Study
-
Experience
-
Instruments and Software
-
FAQs
-
Related Resources
-
Related Services
Overview
MetID team utilizes ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) coupled with a photodiode array detector (PDA) and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) to search for and identify the metabolites generated in incubation systems, which can provide three types of routine assays based on different purposes, including metabolic soft-spot analysis, reactive metabolite trapping and cross-species metabolism comparison. Meanwhile, WuXi AppTec DMPK can provide some special types of assays or methods, such as acidified S9/lysosomal systems used for antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), metabolite matching, hydrogen/deuterium (H/D) exchange and titanium trichloride reduction assays used to confirm the metabolite structure.
Learn More


Assays
Case Study
-
Metabolite Profiling and Identification of Compound A (Commercially Available) in Rat, Dog, Monkey, and Human Hepatocytes
A total of eight metabolites (M1-M8) were detected and identified by LC-UV-HRMS after incubated in rat, dog, monkey, and human hepatocytes for 120 minutes. The LC-UV (λ: 270-360 nm) chromatograms and the relative abundance of compound A and its metabolites were summarized in Figure 1 and Table 1, respectively.
Compared with animal species, the metabolites formed in incubation of human hepatocytes were detected in hepatocytes of at least two animal species. In human hepatocytes, M1, M6 and M8 were considered to be the top three metabolites, while the relative abundance of M6 in all animal species was less than 1% which may due to further glucuronidation of M6. By comprehensive comparison with animal species, the metabolite profiling of compound A in human hepatocytes was similar to that in dog hepatocytes. Considering the similarity of metabolism in vitro, dog is a suitable large animal species for toxicological evaluation of compound A.
Learn More
-


Metabolite profiles (LC-UV) of Compound A in rat, dog, monkey, and human hepatocytes
Figure 1
-


The relative abundance of compound A and its metabolites in rat, dog, monkey, and human hepatocytes
Table 1
-
Experience
-
16+
Years of experience
-
500+
Submissions of IND applications
-
8000+
Screening projects
Instruments and Software
-
-


Thermo Orbitrap Eclipse™ Tribrid™
-


Thermo Orbitrap Exploris™ 480
-


Thermo Q-Exactive™ HF
-


Waters VION™ IMS QTof
-


Thermo Q-Exactive™ Plus
-


Thermo Q-Exactive™
-


Therno LTQ Orbitrap XL
-


Waters Xevo®G2 QTof
-


Solid scintillation counter: off-line detection of radioactivity
-


Liquid scintillation counter: total radioactivity detection
-


On-line detection of radioactivity
-
-
-


Thermo Scientific™ Compound Discoverer™
-


Thermo Scientific™ Mass Frontier™
-


Thermo Scientific™ Metworks™
-


Waters MetaboLynxTM
-


Mass Analytical Mass-MetaSite
-


Waters UNIFI®
-


Thermo Scientific™ Biopharma Finder™
-
FAQs
Related Resources




-


Software-aided Detection and Structural Characterization of Cyclic Peptide Metabolites in Biological Matrix by High-resolution Mass Spectrometry
PublicationsJan 09, 2026Learn More -


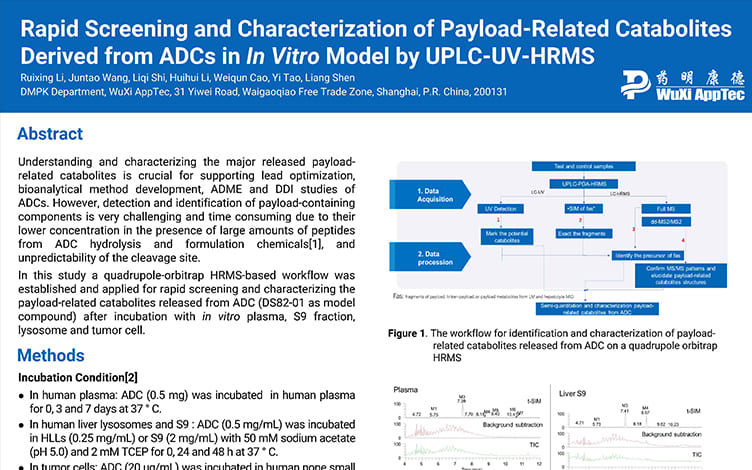
Rapid Screening and Characterization of Payload-Related Catabolites Derived from ADCs in In Vitro Models by UPLC-UV-HRMS
PostersOct 22, 2025Learn More -


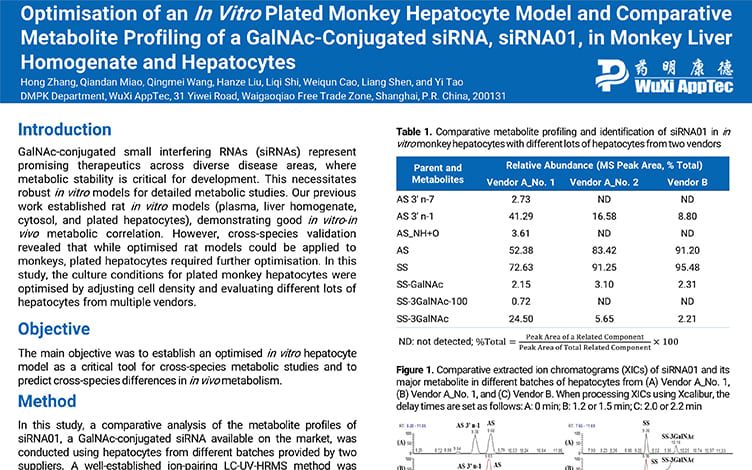
Optimisation of an In Vitro Plated Monkey Hepatocyte Model and Comparative Metabolite Profiling of a GalNAc-Conjugated siRNA, siRNA01, in Monkey Liver Homogenate and Hepatocytes
PostersSep 26, 2025Learn More -


Detection and Characterization of In Vitro Payload-Containing Catabolites of Noncleavable Antibody-Drug Conjugates by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Multiple Data Mining Tools
PublicationsApr 28, 2025Learn More -


Prodrug Approaches for Improved DMPK Characteristics and Their Preclinical Study Considerations
ArticlesAug 29, 2024Learn More -


Development of a Convenient In Vitro Method for Predicting Metabolism and Disposition of Acrylamide Covalent Drugs in Humans
PostersMar 21, 2024Learn More -


Effect of pH on Metabolite Profiling and Identification of GalNAc Conjugated siRNA in In Vitro Metabolic System
PostersJan 23, 2024Learn More -


Metabolite Profiling and Identification of Oligonucleotide in In Vitro Metabolic System
PostersOct 30, 2023Learn More
Stay Connected
Keep up with the latest news and insights.