-
Overview
-
Study Models and Platforms
-
Study Strategies
-
Case Study
-
FAQs
-
Related Resources
-
Related Services
Overview
WuXi AppTec DMPK has accumulated rich project experience in in vitro ADME, metabolite identification, and radiolabeled ADME of covalent drugs. Combining with the characteristics of covalent drugs, we have specially established a series of research platforms for covalent drugs.
Learn More

Study Models and Platforms
-
High-resolution mass spectroscopy (HRMS) platform
Intact protein technology uses high-resolution mass spectroscopy to determine the precise molecular weight of protein. When the target protein covalently binds to small molecular compounds, the molecular weight of the protein increases, which can directly characterize the binding situation. The method has the advantages of simple development, high throughput and good reproducibility. WuXi AppTec DMPK can provide screening services for covalent drugs based on HRMS, including screening related compounds such as covalent molecular glue and covalent PROTAC* (Proteolysis-targeting chimera), and identifying binding sites.

-
In vitro ADME platform
Because of the possible reactivity between the chemical warhead and plasma protein, the conventional test methods may lead to low reliability of fu value, especially those covalent drugs with serious nonspecific binding problems. By optimizing methods, such as low temperature, diluting plasma, ultracentrifugation or flux dialysis, we can determine the plasma protein binding rate of covalent drugs with low stability in plasma, and get a more reliable fu value.
According to the characteristics of covalent drugs, other experiments were established to evaluate the distribution and metabolism of covalent drugs in vitro, such as HSA binding experiment, HSA stability experiment, GSH binding experiment and GSH stability experiment catalyzed by GST enzyme.

-
Metabolite identification platform
WuXi AppTec DMPK can provide comprehensive services of metabolite profiling and structure identification, analyze, separate and identify metabolites in biological matrix, and deeply understand the possible metabolic and clearance pathways of covalent drugs. Combined with the characteristics of covalent drugs, we mainly use GSH-containing liver microsomal incubation system to detect the metabolites of covalent drugs under the action of CYP enzyme, electrophilic warheads and/or products of reactive metabolites combined with GSH. Liver S9/cytosol and blood incubation system were used to investigate the electrophilic reaction products mediated by glutathione transferase. Plasma or albumin incubation system was used to evaluate the degree of covalent binding between covalent drugs and albumin.

-
Radiolabeled ADME platform
WuXi AppTec DMPK can accurately determine the binding rate of covalent drugs and their metabolites or reactive metabolites intermediates with proteins by using radioactive labeling technology. Combined with HRMS and enzymatic hydrolysis technology, the possible forms of binding moiety can be analyzed, such as the binding of original drugs or metabolites, the types of proteins bound, and the binding sites.
Moreover, the 14C-labeled drugs can be directly synthesized in WuXi AppTec, and a reasonable labeling site can be designed according to the chemical structure, synthesis process and early unlabeled metabolite identification results.

Study Strategies
-
DMPK study strategies of covalent drugs
The DMPK strategy of covalent drugs is similar to that of conventional small molecules. However, due to covalent binding, special assay design or methods are needed to figure out its distribution and metabolism properties. In terms of distribution, fu may be unreliable due to low recovery resulting from covalent binding with plasma protein reversibly or irreversibly. Except for metabolism via CYP P450, covalent drugs may be eliminated through binding with plasma protein, or conjugated with GSH mediated by GST enzyme, which potentially bring about the issue of GST phenotyping. Covalent binding with liver protein could cause TDI liability or toxicity, which should be paid attention in early stage.

Case Study
-
-

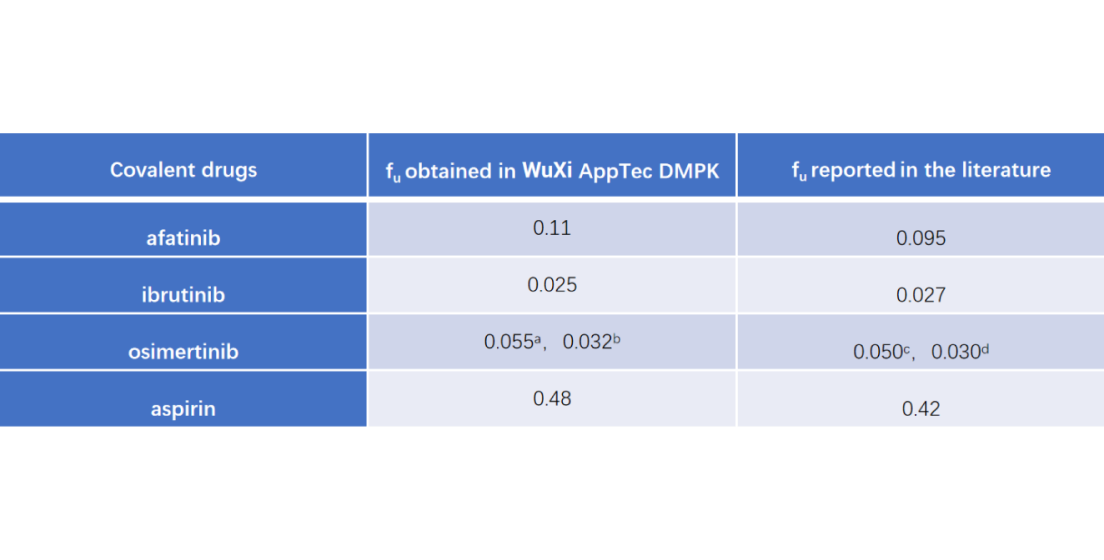
aflux dialysis method at 37 °C. bultracentrifugation at 4 °C.cPharmocology review. dJ Pharm Sci. 2020;109(10):3181-3189.
Due to the possible reactivity between warheads and plasma proteins, conventional methods to measure fu may be unreliable resulted from low recovery. By optimizing the methods, such as lowering temperature, diluting plasma, or using alternative methods, such as ultracentrifugation or flux dialysis, more reliable fu could be obtained. The table compares the data of four covalent drugs in human plasma generated in WuXi AppTec DMPK with the reported values in the literature.
Learn More
-
FAQs
-
What are covalent drugs?
Covalent drugs incorporate a mildly reactive warhead that forms a covalent bond with protein targets to confer additional affinity beyond the non-covalent interactions involved to inhibit target protein.
-
What’s the advantage of covalent drugs comparing to conventional small drugs?
The advantages of covalent drugs are listed below, comparing to conventional small drugs.
High biochemical efficiency of covalent drugs may translate to lower doses and reduced off-target effects.
Nonequilibrium binding of covalent drugs might help to overcome competing endogenous substrate concentrations that bind to the same target site.
Covalent binding might mitigate the development of drug resistance resulting from mutation of a binding site.
Covalent drugs can potentially address targets with shallow, undruggable binding sites.
Covalent drugs may prolong duration of action.
-
What are the challenges of covalent drugs in DMPK Study?
Covalent drugs may bind with serum albumin or other non-target proteins, which makes it difficult to determine the distribution and clearance of without radiolabeled compounds in screening stage.
Compared with conventional small molecule drugs, the PK/PD of covalent drugs is more challenging.
Related Resources




-


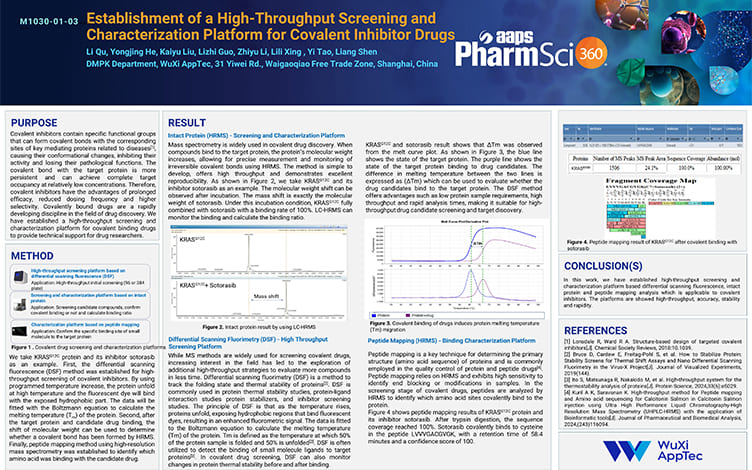
Establishment of a High-Throughput Screening and Characterization Platform for Covalent Inhibitor Drugs
PostersNov 21, 2025Learn More -


A Robust LC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Covalent Drugs in Mouse Blood
PostersJul 10, 2025Learn More -


Discovery and Evaluation of Pyrazolo[3,4‑d]pyridazinone as a Potent and Orally Active Irreversible BTK Inhibitor
PublicationsMay 15, 2025Learn More -


Covalent Drugs DMPK Services
BrochuresApr 10, 2025Learn More -


Unlocking High-Throughput Bioanalysis of Covalent Drugs with Intact Protein, DSF, and Peptide Mapping Techniques
ArticlesJan 20, 2025Learn More -


Successful Prediction of Oral Pharmacokinetics of the KRAS G12C Inhibitor MRTX-849 in Humans Using PBPK Modeling
PostersDec 03, 2024Learn More -


Establishment of Two In Vitro Glutathione Conjugation Models and Their Application in Covalent Drugs
ArticlesOct 12, 2024Learn More -


Development of a Convenient In Vitro Method for Predicting Metabolism and Disposition of Acrylamide Covalent Drugs in Humans
PostersMar 21, 2024Learn More
Stay Connected
Keep up with the latest news and insights.