-
Overview
-
Study Models and Platforms
-
Experience
-
Assays
-
Instruments
-
Case study
-
FAQs
-
Related Resources
-
Related Services
Overview
Based on the pharmacokinetics evaluation systems for PROTAC molecules, WuXi AppTec DMPK has supported the screening of tens of thousands of PROTACs molecules and the IND applications of dozens of PROTAC molecules. In this process, we have formed a unique methodology for PROTAC pharmacokinetic studies - aimed at helping drug developers rapidly advance their PROTAC drug development projects. We have accumulated rich experiences in various aspects of PROTAC, including preclinical formulation screening, in vivo pharmacokinetic experiment design, in vitro experiment model selection, bio-sample analysis speed, in vivo and in vitro metabolite identification capability, etc. We also have notable advantages in pharmacokinetic research strategy and data interpretation, which can effectively shorten the development cycle of PROTACs.
Learn More

Study Models and Platforms
-
In vitro transporter model of PROTAC
For PROTACs, it is important to note that choosing an unsuitable model can lead to wrong results. For example, the use of the Caco-2 model may underestimate the inhibitory effect of PROTACs on efflux transporters because most PROTACs have limited permeability, resulting in low intracellular concentrations. In this case, the membrane vesicle model can be used instead as PROTACs can directly interact with the transporter outside the membrane to obtain more accurate data. Please refer to the case shown as below.
-
Metabolite identification model of PROTAC
WuXi AppTec DMPK has a variety of metabolite identification models and has a wealth of experience in model selection. According to your research purpose and the structural characteristics of specific molecules, we can employ the appropriate in vitro metabolic system to meet your research needs.

-
PROTAC biological sample analysis platform
WuXi AppTec DMPK Non-GLP bioanalysis team has an integrated and fully capable bioanalysis platform, which can provide bioanalysis services for various innovative molecular entities throughout the pre-clinical stages of drug development. Among them, we have years of experience in performing PROTAC bioanalysis using the LC-MS/MS platform. In cooperation with numerous clients, we have completed the analysis of hundreds of thousands of biological samples, accelerating the research and development speed of clients' PROTAC drugs.

Experience
-
9+
Years’ experience in bio-analysis
-
1000+
PROTAC molecules per year
-
15+
IND filing molecules
-
100+
Global clients of PROTAC
Assays
EXPLORATORY Lead Molecule Optimization | PRE-CLINICAL IND Enabling and IND Filing | CLINICAL NDA Filing | |
ADME | Log D Solubility(FeSSIF, FaSSIF, SGF) Caco2/MDR1-MDCK Permeability Plasma protein binding Hepatocyte stability Liver S9, microsome, AO metabolic stability Blood/plasma stability | Caco2/MDR1-MDCK Permeability Plasma protein binding Liver microsome/hepatocyte stability Metabolite identification across species ADME study of radiolabeled compounds Metabolite identification in plasma, urine, feces, bile from toxicological species | Metabolite identification in plasma, urine, feces from human |
DDI | Enzyme inhibition | Enzyme inhibition and induction Enzyme Phenotyping Transporter inhibition Transporter substrate | Other transporter substrates PBPK method predicts DDI risk in human Clinical DDI Research |
PK/TK | Testing of biomarkers in PD or PK studies in toxicological species Excretion study | PK study in toxicological species Tissue distribution studies Urine, fecal and bile excretion studies PK study TK research | Human PK studies Population PK study in human |
Instruments
Due to the complex molecular structure, PROTACs with chiral centers are common. Chiral Analysis is one of the main challenges in Chiral Drug Development. In WuXi AppTec DMPK, both UPLC and UPCC methods are available for Chiral Analysis. We also have established a Chiral Column Library, which helps to shorten the time for method development.
-
-


UPLC-MS/MS
-


UPCC-MS/MS
-


Chiral Column Library
-
Case study
-
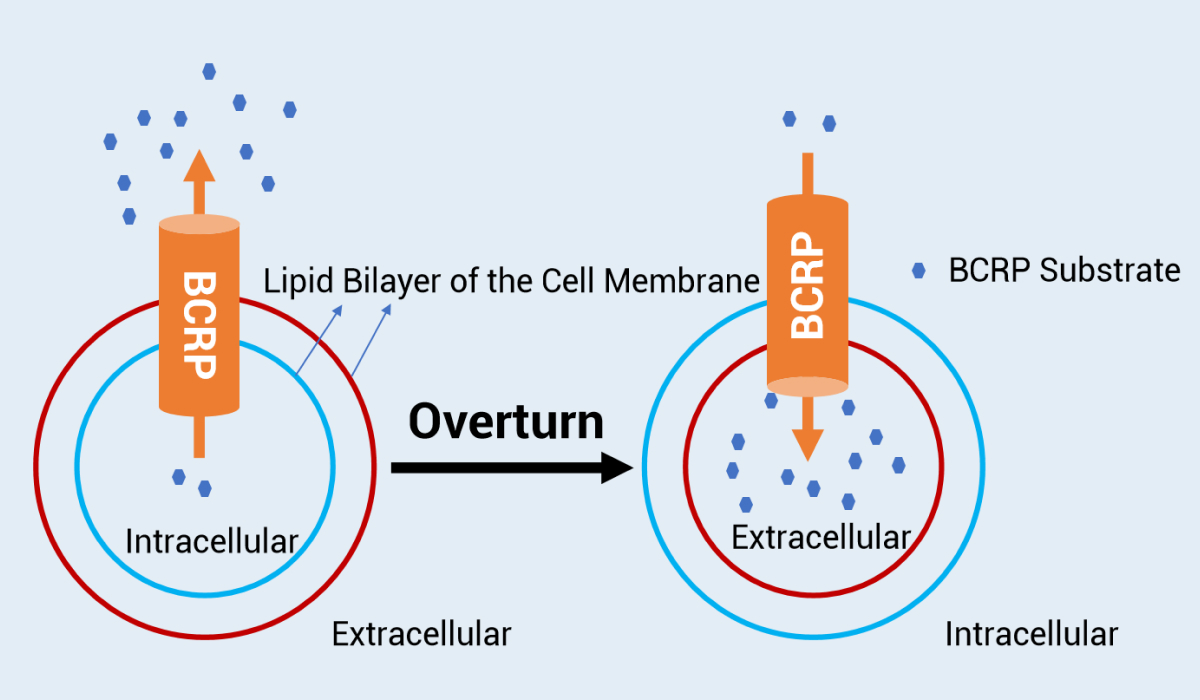
PROTAC Transporter Inhibition Evaluation
Background: BCRP (Breast Cancer Resistance protein) is an important ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter. BCRP is mainly expressed in the apical membrane of the intestinal epithelia, in the bile duct side of hepatocytes, and in the blood-brain barrier near the blood, which can have a significant impact on restricting the entry of BCRP substrates into intestinal epithelia, mediating drug biliary excretion and the blood-brain barrier 1. A client needed to evaluate the inhibition of BCRP by PROTAC molecules. Preliminary results showed that the molecule had no significant inhibition of BCRP (IC 50 > 100 μM). However, the PROTAC molecule was reported in the literature to inhibit BCRP, so the client sought assistance and explanation.
Customized Design: After receiving questions from the client, we evaluated the study methods and data. Based on what we know about PROTAC molecules, PROTAC generally has poor permeability. With the routine cell model, the extracellular PROTAC concentration is high, while the concentration of drugs entering the cell may be very low. Therefore, we recommended the BCRP-expressing inside-out membrane vesicles model for the evaluation of BCRP inhibition. The transport direction of the BCRP-mediated substrates is from the outer membrane to the inner membrane, and thus PROTAC could directly bind to the BCRP transporter outside the membrane.
Results: The vesicle method showed that the PROTAC molecule had a strong inhibitory effect on BCRP, which was consistent with the previous literature reports. Compared with conventional methods, which cannot obtain an inhibitory window, the vesicle method is more sensitive in the evaluation of efflux transporter inhibition. In addition to the BCRP transporter, the vesicle method was also recommended for the evaluation of the inhibition of other efflux transporters by PROTAC molecules.
Learn More
-

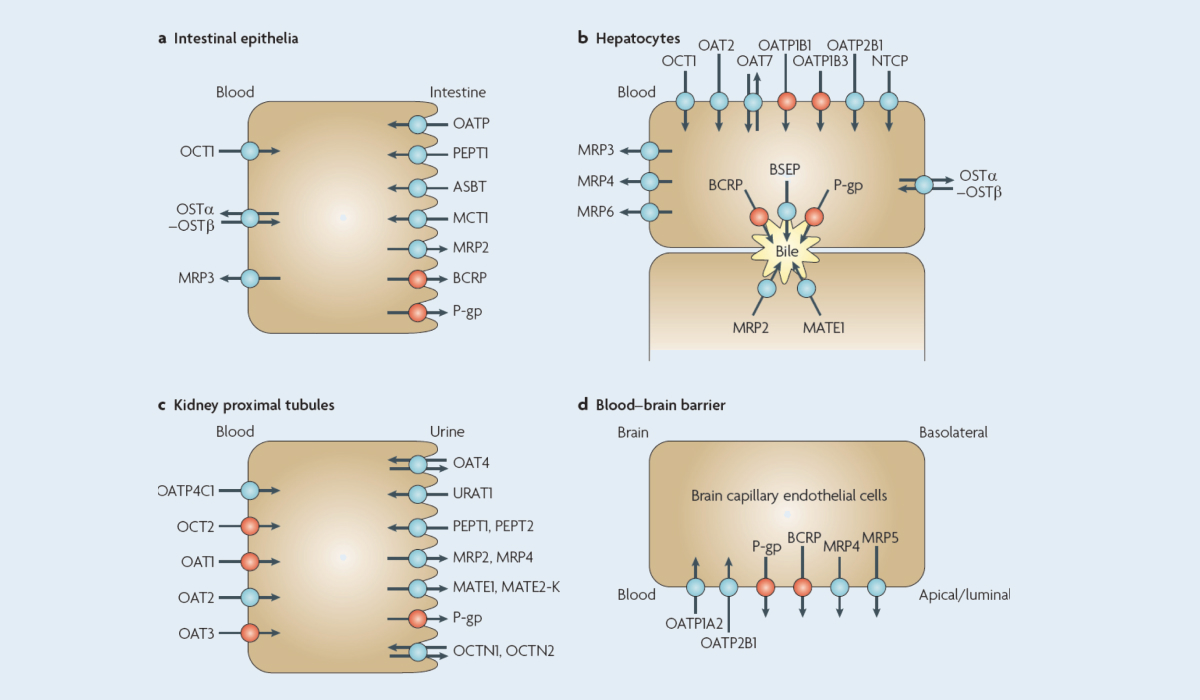
Human transport proteins for drugs and endogenous substances1
-

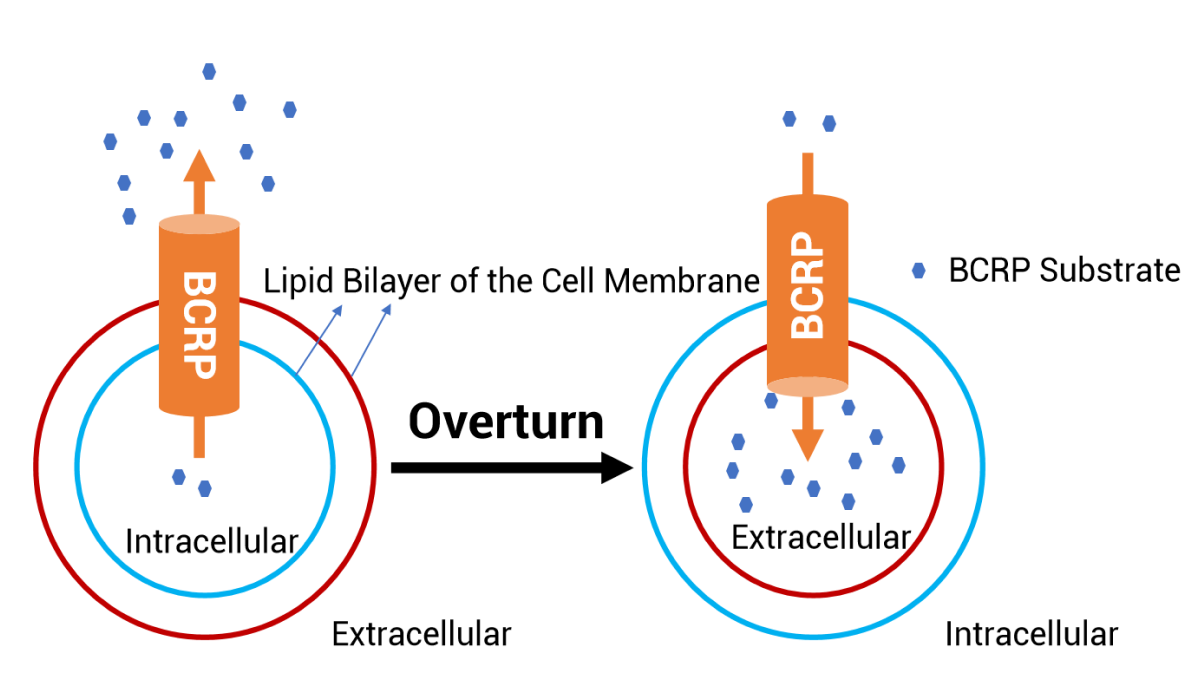
The schematic diagram of whole-cell model and valgus vesicles mode
-
FAQs
-
What is a Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)?
PROTAC utilizes the body’s natural protein degradation mechanism, namely the ubiquitin-proteasome system. As a bifunctional molecule, PROTAC consists of three key structural parts: a ligand used to bind the target protein; a ligand binding the ubiquitin-protein ligase (E3); and a linker connecting the two ligands.
*On this page, PROTAC specifically refers to the abbreviation of PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera as the therapeutic modality.
-
What is the difference between PROTACs and traditional small molecule inhibitors?
Due to its unique structure, PROTAC induces E3 ligase to label the target protein with ubiquitin by bringing the E3 ligase and the target protein into proximity, promoting the degradation of the target protein, and the PROTAC molecules that fall off after the target protein degradation can continue to be recycled. Different from the occupancy drive pharmacology of most small molecule drugs, PROTAC can access previously inaccessible proteins without occupying an active pocket and relying on target occupancy to disrupt target protein, this is known as event-driven pharmacology.
-
What studies are recommended for the early DMPK evaluation of PROTAC molecules?
The early DMPK evaluation of PROTAC molecules can be roughly divided into the following parts: One part is to characterize the basic DMPK properties of compounds, including the determination of physical and chemical properties, in vitro permeability detection, plasma protein binding and preliminary in vitro drug interaction tests. The other part is further screening optimization of compounds, focusing on the determination of solubility and in vitro metabolic properties (including qualitative and quantitative studies). The selected compounds will be advanced to in vivo PK studies in rodents to further evaluate the DMPK properties of the compounds.
-
Is it necessary to conduct an additional set of toxicological studies if fracture metabolites appear in the metabolic studies of PROTAC molecules?
Relevant technical guidelines for the safety evaluation of metabolites can also be applied to the evaluation of PROTAC molecules. If the relevant conditions are met, it is recommended to carry out toxicological evaluation of metabolites.
-
Studies on the permeability of PROTAC molecules in vitro have shown poor permeability. Does it indicate that their absorption in vivo will also be poor?
Whether poor permeability of PROTAC molecules in vitro predicts poor absorption in vivo has not been supported by a large amount of data. Our experience is that PROTAC molecules that show hypotonic in vitro may also achieve moderate bioavailability in animals, and therefore caution is recommended in the use of in vitro permeability data for screening PROTAC compounds. On the other hand, due to the characteristics of PROTAC molecules, there are many challenges in the in vitro testing of PROTACs (such as low solubility, strong non-specific adsorption, etc.), so it is also very important to select and optimize the relevant in vitro testing system for the study of PROTAC molecules.
-
What is the basis for the selection of PROTACs molecular preclinical toxicological species? Does the large animal species have to be the monkey?
PROTACs still belongs to the category of small molecule compounds, so it can follow the species selection method for the toxicology of small molecule compounds, that is, the principle of similarity between metabolism and human ancestry, while certain pharmacological effects are also need to be considered at the same time. Toxicological species of PROTAC do not always need to be monkeys.
-
What are the key points that need to be noted or shared in the in vivo PK study of PROTAC molecules in the screening stage?
In the early screening stage, in vivo PK studies in animals, it’s suggested to use clear solutions to avoid poor absorption due to solubility, and it is recommended to investigate the difference between fasted and fed exposure. Sometimes fed condition is conducive to oral absorption of PROTAC molecules. In terms of bioanalysis, attention should be paid to the non-specific adsorption of PROTAC molecules, low sample recovery and potential stability problems in the matrices.
Related Resources




-


Evaluation of Clearance Prediction Methods for Vepdegestrant (ARV-471) Using PBPK Modelling: Insights into PROTAC Clinical Pharmacokinetics
PostersSep 11, 2025Learn More -


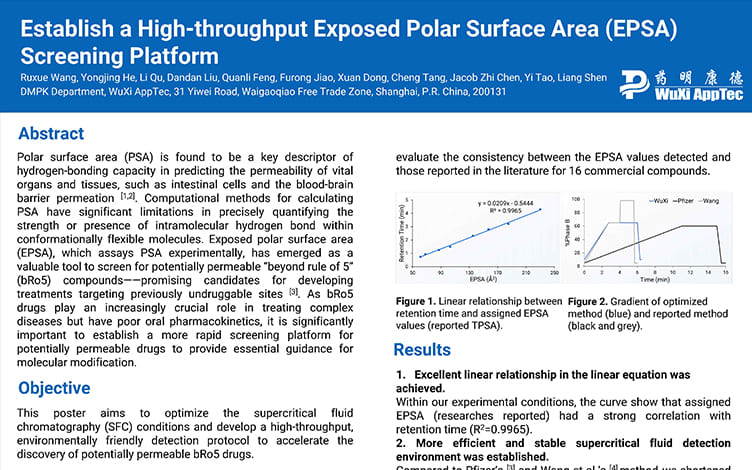
Establish a High-throughput Exposed Polar Surface Area (EPSA) Screening Platform
PostersSep 04, 2025Learn More -


Sample Chapter: Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras (PROTACs) from Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics: Frontiers, Strategies, and Applications
PublicationsJun 06, 2025Learn More -


Enhancing Permeability Through Exposed Polar Surface Area (EPSA) for Beyond Rule of Five (bRo5) Drug Candidates
ArticlesApr 10, 2025Learn More -


Research Strategy of Chiral PROTACs in Discovery Stage Based on Analysis Platforms of UPCC-MS/MS and UPLC-MS/MS
PostersMar 29, 2024Learn More -


Choosing Appropriate Model to Assess PROTAC Drug-Drug Interactions with Efflux Transporters
BlogsJul 26, 2023Learn More -


Overcoming Challenges of PROTAC Bioanalysis to Unleash the Potential
BlogsJul 14, 2023Learn More -


How to Address the Challenges of PROTAC Metabolism
BlogsJul 13, 2023Learn More -


How MetID Studies can Improve Safety and Efficacy in PROTAC Drugs
ArticlesJul 07, 2023Learn More -


How to Evaluate PROTAC Drug-Drug Interactions with Efflux Transporters
ArticlesJul 07, 2023Learn More -


PROTAC Bioanalysis: Challenges and Strategies
ArticlesJul 07, 2023Learn More -


Research on PROTAC Druggability: Solubility and Permeability
ArticlesJun 30, 2023Learn More -


An Overview of PROTAC Technology and DMPK Research Strategy
ArticlesJun 30, 2023Learn More -


Research on PROTAC Metabolism: Strategies and Main Approaches
ArticlesJun 25, 2023Learn More -


How to Improve PROTACs' Oral Bioavailability
BlogsMay 24, 2023Learn More -


DMPK Optimization of Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras (PROTAC)
WebinarsMay 04, 2023Learn More -


PROTAC Brightens Disease Treatments: An Overview of the PROTAC Research, Challenges, and DMPK Solutions
BlogsMay 04, 2023Learn More -


Preclinical Drug Development Testing for Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)
BrochuresMay 04, 2023Learn More
Reference
- 1.
GIACOMINI K M, HUANG S M, TWEEDIE D. Membrane transporters in drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2010, 9(3): 215-236.
Stay Connected
Keep up with the latest news and insights.