-
Overview
-
Metabolism-mediated Drug Interactions
-
Transporter-mediated Drug Interactions
-
Case Study
-
Experience
-
FAQs
-
Related Resources
-
Related Services
Overview
Evaluating the DDI potential of an investigational new drug often starts with in vitro experiments. The data generated from in vitro DDI studies can support both IND (Investigational New Drug) and NDA (New Drug Application) submissions. To ensure the accuracy and reliability of our experimental data, in vitro test systems used in the DDI studies have been validated and controlled by the positive commercial compounds recommended by the regulatory authorities.
WuXi AppTec DMPK can fully support in vitro DDI packages for submission to the regulatory authorities mentioned above with thousands of cases.
Learn More


Metabolism-mediated Drug Interactions
Evaluating the enzyme-mediated DDI potential of an investigational new drug involves (1) identifying the principal routes of the drug’s elimination, (2) estimating the contribution of enzymes to the drug’s disposition, and (3) characterizing the effect of the drug on enzymes. WuXi AppTec DMPK offers a suite of services to examine enzyme-mediated DDIs, which includes assays for cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibition, CYP time-dependent inhibition, CYP induction (enzyme activity and/or mRNA evaluation, along with RIS assessment), UGT induction and UGT inhibition, as well as various other non-CYP mediated metabolism assays. Furthermore, WuXi AppTec DMPK provides a comprehensive Ki service to measure the inhibitor's affinity for the enzyme and identify the inhibition type. They also offer a kinact/KI service to delve deeper into time-dependent inhibition characteristics. Additionally, WuXi AppTec DMPK delivers a CYP and UGT reaction phenotyping service, along with other enzyme-mediated reaction phenotyping services.
Learn More

The more detailed assay types are listed below:
-
Inhibition of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes
CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A
Direct inhibition
IC50 determination using discrete/ 5 in 1 cocktail / 7 in 1 cocktail probe substrate, Ki or Ki,u determination using discrete probe substrate.
Time-dependent inhibition
IC50 shift or AUC shift determination using discrete probe substrate, Kinact/KI determination using discrete probe substrate.
-
Induction of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes
Reporter Assay System
Human Hepatocyte System (CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A)Enzyme activity and/or mRNA assessment
EC50 and Emax assessment
RIS assessment
-
Reaction Phenotyping
Phenotyping of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes
Phenotyping of UDP-Glucuronosyl transferases
Aldehyde oxidase (AO), carboxylesterase (CES), monoamine oxidase (MAO), flavin monooxygenase (FMO), xanthine oxidase (XO), and alcohol/aldehyde dehydrogenase (ADH/ALDH) enzymes

-
UGT-mediated DDIs as an inhibitor or inducer
UGT inhibition evaluation
IC50 determination using recombinant human UGT enzymes / human liver microsome.
UGT induction evaluation
mRNA assessment.

Transporter-mediated Drug Interactions
Our in vitro transporter platform offers various models for assessing transporter-mediated DDIs. Substrates or inhibitors of specific transporters can be determined using three types of cell-based models, including 1) Caco-2 cells expressing efflux transporters such as P-gp and BCRP, and 2) MDR1-MDCK I and MDR1-MDCK II cells specifically expressing P-gp, are used for DDI studies with P-gp. MDR1 MDCK I cell line, which holds promise to better predict P-gp substrates at the blood-brain barrier in vivo, is mainly used in CNS drug development. 3) Transfected HEK293 cells with specific transporter genes (human OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2-K, PEPT1, PEPT2, and NTCP) for DDI studies with SLC transporters. In addition, we offer membrane vesicles for investigating ABC transporters including P-gp, BCRP, BSEP, and MRP1/2/3/4. Primary hepatocytes have been used in the present DDI investigation for a comprehensive assessment of hepatic uptake. For more details on transporter-related drug interaction services, please refer to our Permeability and Transporter Study page.
Case Study
-
Data from Cytochrome P450 Inhibition Assay
Known CYP inhibitors were screened in WuXi AppTec DMPK's Cytochrome P450 Inhibition assay in 3 separate systems. All the systems are well characterized in vitro test systems. The IC50 values obtained from the 7-in-1 substrate cocktail approach and the single substrate approach are illustrated in Figure 1. The data from these approaches were correlated well with the R2 value of 0.995. The IC50 of ten commercial drugs for Cytochrome P450 Isoenzyme by using 5-in-1 cocktail substrates in house vs literature data are also listed in Figure 2. These results showed that the data are correlated well.
Learn More
-

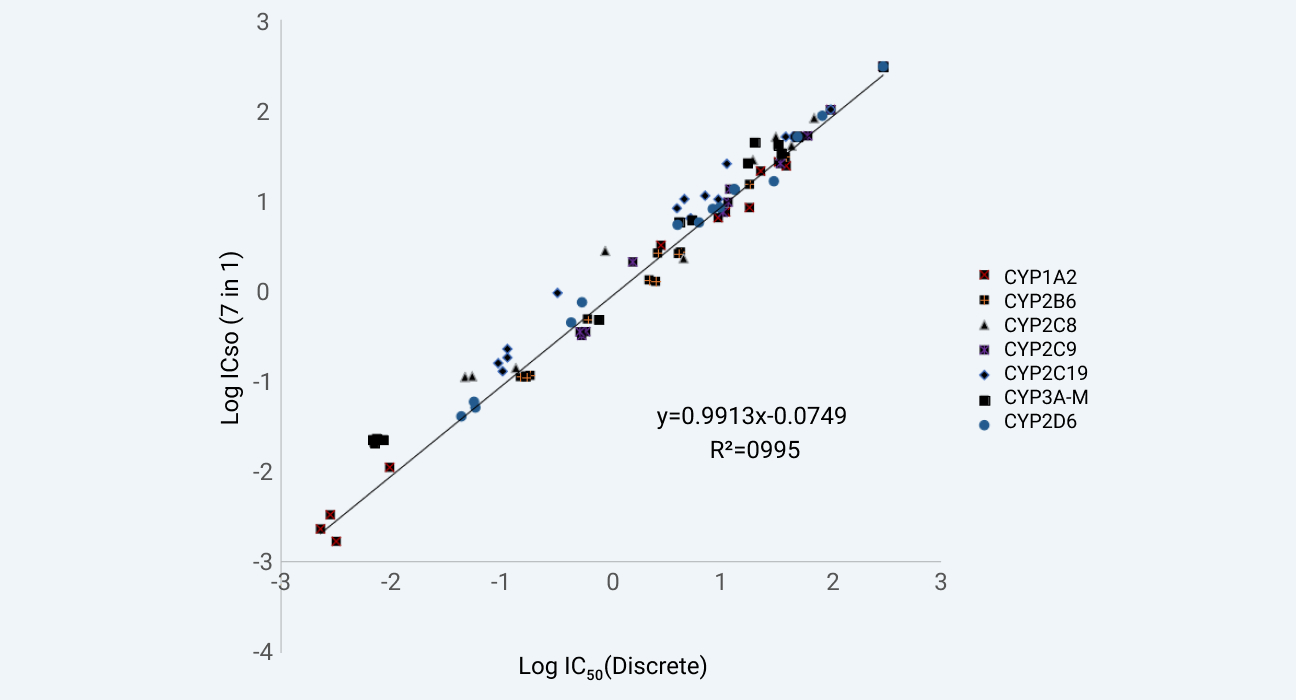
Assay validation of WuXi AppTec DMPK's 7-in-1 CYP inhibition assay against our discrete CYP inhibition assay.
Figure 1
-

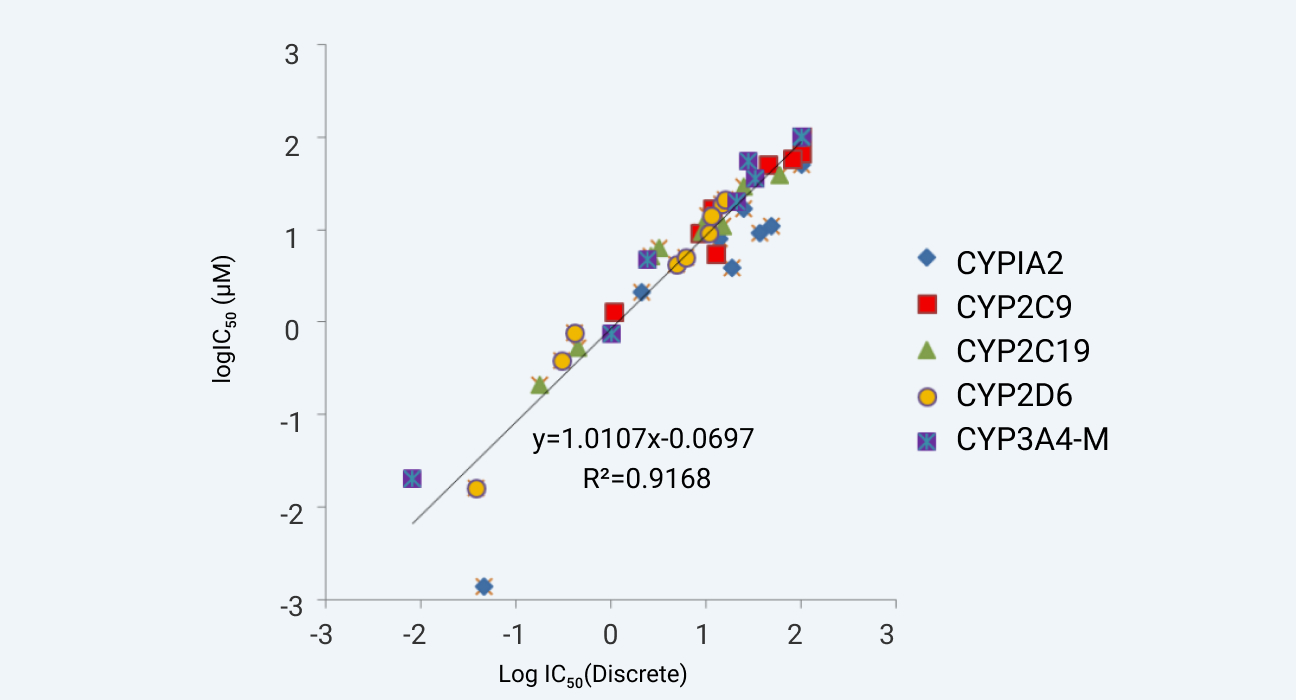
Correlation of IC50 of ten commercial drugs for Cytochrome P450 Isoenzyme by using 5-in-1 cocktail substrates. The abscissa is the Log value of IC50 for internal data, the ordinate is the Log value of IC50 for literature data
Figure 2
-
Experience
-
15+
Years
-
1,500+
Submissions of IND applications
-
3,000+
Screening projects per year
FAQs
-
What is the meaning of drug interaction?
A drug interaction is a reaction between two (or more) drugs or between a drug and a food, beverage, or supplement. Taking a drug while having certain medical conditions can also cause a drug interaction. For example, taking a nasal decongestant if you have high blood pressure may cause an unwanted reaction.
-
mRNA Levels vs. Enzyme Activity Levels: Which Should I Choose for Cytochrome P450 Induction Assays?
1. Based on the iteration of FDA DDI guidance, enzyme activity has always been the simplest and most frequently used endpoint.
2. According to the genetic central dogma, changes in mRNA levels precede changes in enzyme activity levels. Thus, early screening assays can rely only on assessments of the mRNA levels.
3. A single endpoint is susceptible to interference from different factors. Enzyme activity levels are susceptible to misleading results if the investigational drug itself is an inhibitor of that enzyme, while mRNA levels are susceptible to the compound’s potential for down-regulation of gene expression; thus, both endpoints need to be included in the IND-enabling study.
-
What are the types of drug-drug interactions?
Drug-drug interactions (DDIs) can be classified into two major categories based on their mechanisms:
1. Pharmacokinetic (PK) Interactions (more extensively studied in drug development):
Enzyme-mediated: Inhibition or induction of drug-metabolizing enzymes (e.g., CYP450 inhibition/induction, UGT inhibition). A well-known example is grapefruit juice inhibiting CYP3A4 activity, which has been shown to cause adverse effects when co-administered with approximately 85 different medications.
Transporter-mediated: Inhibition of ABC or SLC transporters affecting drug absorption or excretion (e.g., P-gp, OATP1B1 inhibition).
2. Pharmacodynamic (PD) Interactions:
Additive or antagonistic effects between co-administered drugs.
Important consideration: Evaluation should also determine whether the drug itself is a substrate of metabolic enzymes or transporters.
-
When should drug-drug interaction studies be conducted?
According to the ICH M12: Drug Interaction Studies guideline (May 2024), DDI evaluation should be conducted throughout the entire drug development process, consisting of three key stages:
Step 1: Preclinical (In Vitro) Assessment
1. Initial evaluation of DDI potential (object or precipitant drug) through:
1)Metabolic phenotyping to identify primary clearance pathways
2)Enzyme inhibition/induction assessment.
2. Transporter studies using validated systems with probe substrates/inhibitors to determine:
1)Whether the investigational drug is a substrate of key transporters.
2)Inhibitory potential against major transporters (P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2-K)
3)Additional transporters may be evaluated if clinically relevant.
Step 2: Clinical Evaluation
1. Various study designs are available depending on study objectives.
2. May utilize:
1)Dedicated clinical DDI studies (e.g., cocktail studies).
2)Model-based approaches (PBPK or static models) when supported by robust in vitro data.
Step 3: Post-Marketing Surveillance
1. Continuous monitoring of real-world DDI risks.
2. Essential for:
1)Identifying unexpected interactions.
2)Assessing potential increases in adverse effects.
3)Optimizing clinical management recommendations.
Related Resources




-


DDIM vs. TDI in CYP Enzyme Inhibition Studies: Can Results from a CYP Direct Inhibition Assay be Used to Predict Time-Dependent Inhibition Risk?
ArticlesDec 19, 2025Learn More -


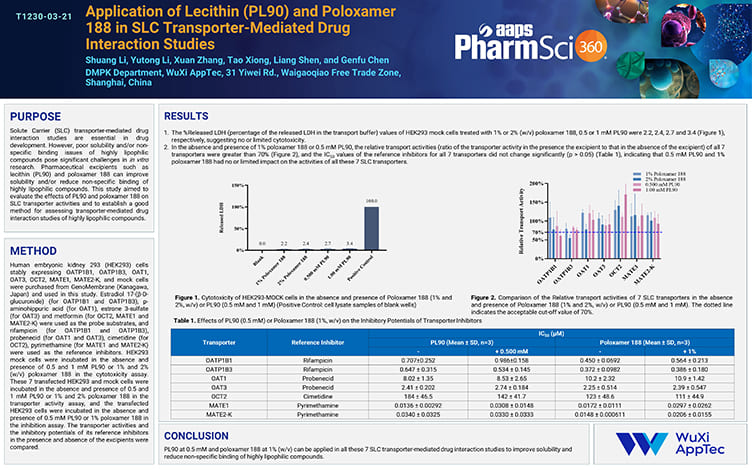
Application of Lecithin (PL90) and Poloxamer 188 in SLC Transporter-Mediated Drug Interaction Studies
PostersNov 21, 2025Learn More -


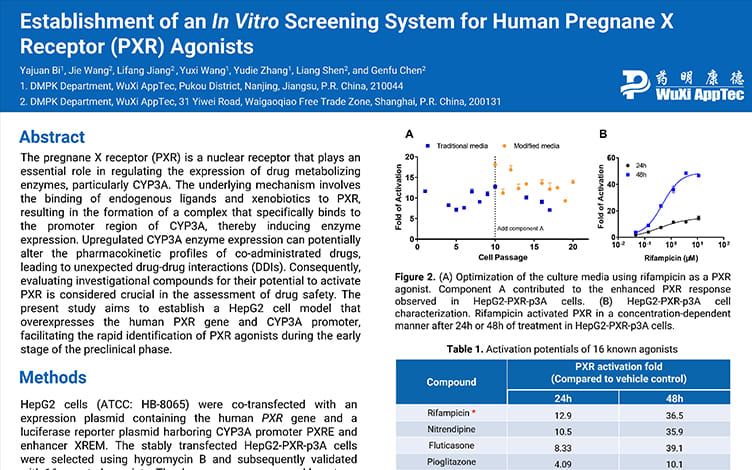
Establishment of an In Vitro Screening System for Human Pregnane X Receptor (PXR) Agonists
PostersNov 07, 2025Learn More -


Decoding the Key Role of Plasma Protein Binding in Drug-Drug Interactions
ArticlesAug 15, 2025Learn More -


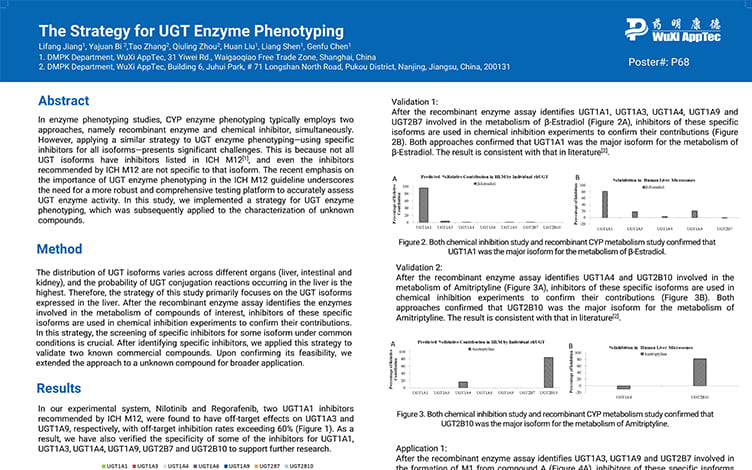
The Strategy for UGT Enzyme Phenotyping
PostersAug 12, 2025Learn More -


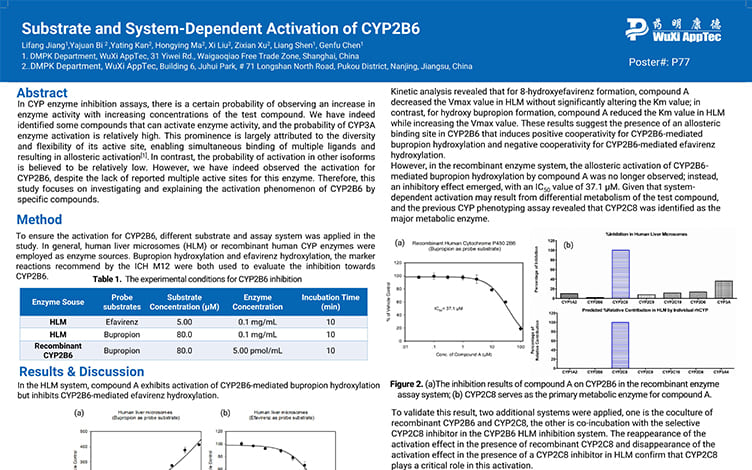
Substrate and System-Dependent Activation of CYP2B6
PostersAug 06, 2025Learn More -


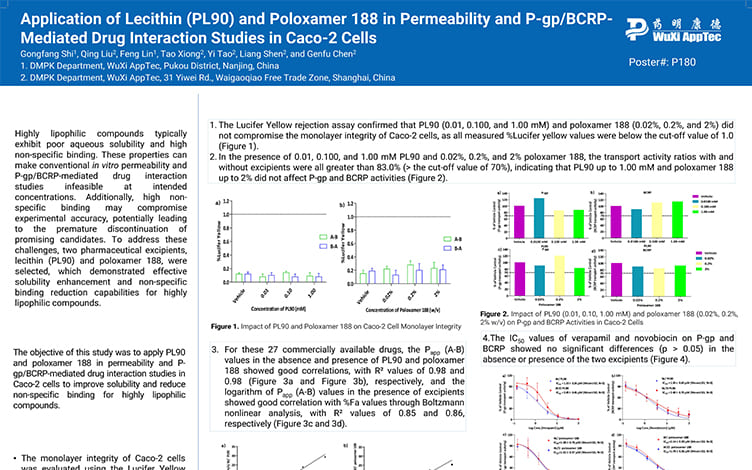
Application of Lecithin(PL90) and Poloxamer 188 in Permeability and P-gp/BCRP-Mediated Drug Interaction Studies in Caco-2 Cells
PostersJul 23, 2025Learn More -


ICH M12 Guideline: 4 Key Updates and Reshaping Framework for Enzyme-Mediated Drug-Drug Interaction Studies
ArticlesJun 27, 2025Learn More -


Cyclic Peptides: FDA-Approved Drugs and Their Oral Bioavailability and Metabolic Stability Tactics
ArticlesMay 08, 2025Learn More -


CYP17A1/19A1 Inhibition Services
BrochuresDec 12, 2024Learn More -


Development of an In Vitro Platform for Screening UGT Inhibitors Using Human Liver Microsomes
PostersOct 12, 2024Learn More -


Is the Dilution Method for Measuring IC50 Shift Values a More Sensitive Approach for Evaluating Time-Dependent Inhibition?
PostersSep 30, 2024Learn More -


A Comprehensive Platform for Evaluating the In Vitro CYP Reaction Phenotyping of New Molecular Entities (NME)
PostersSep 26, 2024Learn More -


The Role of Hepatic Transporters in Drug-induced Liver Injury (DILI) Research and Preclinical Evaluation Recommendations
ArticlesSep 13, 2024Learn More -


Application and Strategy of 3 In Vitro Models for ATP-binding Cassette (ABC) Transporters
ArticlesJul 19, 2024Learn More -


Cytochrome P450 Reaction Phenotyping for 4 Additional CYPs: Why and How?
ArticlesMay 06, 2024Learn More -


Evaluation of Time-dependent Cytochrome P450 inhibition Using the Fully-validated Area Under the Curve Shift Method
PostersApr 30, 2024Learn More -


Evaluation of Cytochrome P450 Inhibition in the 7-in-1 Cocktail Using Preferred Substrates Recommended by Regulatory Agencies
PostersApr 30, 2024Learn More -


mRNA Levels vs. Enzyme Activity Levels: Which Should I Choose for Cytochrome P450 Induction Assays?
ArticlesApr 26, 2024Learn More -


Evidence-Based Strategies for the Characterization of New Chemical Entity (NCE) In Vitro CYP and Non-CYP Enzyme Reaction Phenotyping at the Development Stage
PostersApr 11, 2024Learn More -


How Can More Accurate EC50 and Emax Values Be Obtained in the Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Induction Assays?
BlogsMar 07, 2024Learn More -


Reversible Inhibition vs. Time-dependent Inhibition: 4 Assays for In Vitro CYP Inhibition Evaluation
BlogsFeb 22, 2024Learn More -


The Significance of Accurately Assessing Time-Dependent Inhibition (TDI)
BlogsDec 08, 2023Learn More -


In Vitro Evaluation of CYP450 Time-Dependent Inhibition (TDI): A Novel Area Under the Curve Shift (AUC Shift) Approach
ArticlesNov 17, 2023Learn More -


Choosing Appropriate Model to Assess PROTAC Drug-Drug Interactions with Efflux Transporters
BlogsJul 26, 2023Learn More -


How to Evaluate PROTAC Drug-Drug Interactions with Efflux Transporters
ArticlesJul 07, 2023Learn More
Stay Connected
Keep up with the latest news and insights.