-
Overview
-
Models
-
Case Study
-
FAQs
-
Related Resources
-
Related Services
Overview
The lipophilicity of drugs plays an important role in pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and toxicology. Hence, the study of the lipophilicity of test compounds is helpful in establishing the structure-activity relationship of drugs. In the early stage of drug development, the lipophilicity determination of the test compounds helps researchers find their druggability problems as early as possible and helps to study the ADMET properties of the compounds, which can reduce the failure rate of candidate drugs in the clinical research stage. WuXi AppTec DMPK used the classic Shake-Flask method, reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method, and potentiometric titration method to determine the lipophilicity of the compounds, described by Log D and Log P.
Learn More



Models
-
Shake-Flask Method
Theoretical Concentration
67 μM
Media
1-octanol; 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 (routine), or other pHs
Percentage of DMSO
0.67%
Incubation Equilibration Time
1 h
Equilibration Temperature
Room temperature
Sample Volume Required
20 μL of DMSO stock solution at 10 mM sample concentration
Analytical Method
LC-MS/MS
Turnaround Time
3-5 working days
RP-HPLC Method
Theoretical Concentration
400 μM
Media
50 mM CH3COONH4 in water (pH 7.4);0.25% (v/v) 1-Octanol in methanol
Sample Volume Required
30 μL of DMSO stock solution at 10 mM sample concentration
Analytical Method
HPLC-UV
Turnaround Time
5 working days
-
Test Method
Description
Data Deliverable
Shake Flask
Log D value obtained from 7 different pH values (the general buffer pH range from 1.8 to 12)
Plot Log D vs pH curve to calculate Log P
Log D vs pH (1.8 to 12)
Log P
Chromatography
Log P value is calculated from the residence time of the compound on the column
Log P
Potentiometric Titration
Measurement of pKa
Calculate Log P by the pKa curve
Log P
Case Study
-
For compounds with Log P values within the range of -2~4, the conventional Shake-Flask method is the classic determination method and the gold standard. The characteristic of this method is fast and accurate. However, since the properties of the compounds studied became more and more complex, for example, the number of compounds with Log P >5 is dramatically increased, it is necessary to explore new method to determine the Log P values of new special or complex compounds. For high lipophilicity compounds (Log P >5), WuXi AppTec DMPK established a chromatographic method for the determination of high lipophilicity compounds, which can quickly and accurately obtain the Log P value of test compounds. Part of the validated data for some commercial compounds are shown below:
-


Linear fitting of the standard equation using Method 1
Figure 1
-


Linear fitting of the standard equation using Method 2
Figure 2
-
FAQs
-
What is the main difference between Log D and Log P?
Log D: The degree of drug ionization in solution ranges from 0 to 100%, depending on the pKa of the compound and the pH of the aqueous phase;
Log P: All drugs in the solution are neutral molecules.
-
Why is either too high or too low Log P not good for absorption?
When oral drugs permeate through passive diffusion, it is generally considered that compounds of medium Log P (range 0~3) have the best gastrointestinal absorption. If Log P is too low, the passive diffusion permeation of the compound is low. However, if Log P is too high, the solubility of the compound is poor, and low solubility leads to poor absorption and bioavailability of the compound.
-
For compounds with too high or too low lipophilicity, how can we get more accurate results when using the shake-flask method?
Compounds with high lipophilicity usually have non-specific absorption issues. For these compounds, low-bonding consumables can be used to replace ordinary consumables during the experiment.
For compounds with too high or too low lipophilicity, the instrumental response in the two-phase will be significantly different (or even no response in one phase). In terms of these cases, the solutions are that the incubation concentration can be appropriately increased, or the volume ratio of two phases and the dilution ratio of sample for two phases can be adjusted to improve the instrumental response of the compound in the lower distribution phase.
-
What are the differences between different methods for the Log P determination?
Methods for Log P determination
Range(Log P value)
Interference
Speed
Compound amount
Reproducibility
Predictability
In silico method
Wide
- Fast
- - ★
Shake flask method
-2~4
Not applicable to compounds that tend to degrade; There is a strict requirement for purity
Fairly Fast
Small
★★
★★★
RP-HPLC method
0~6
Mild, not sensitive to impurities
Fast
Small
★★★
★★
Potentiometric titration method
Fairly wide
Limited by solubility
Time-consuming
Large
★★★
★★★
★indicates the grade
Related Resources




-


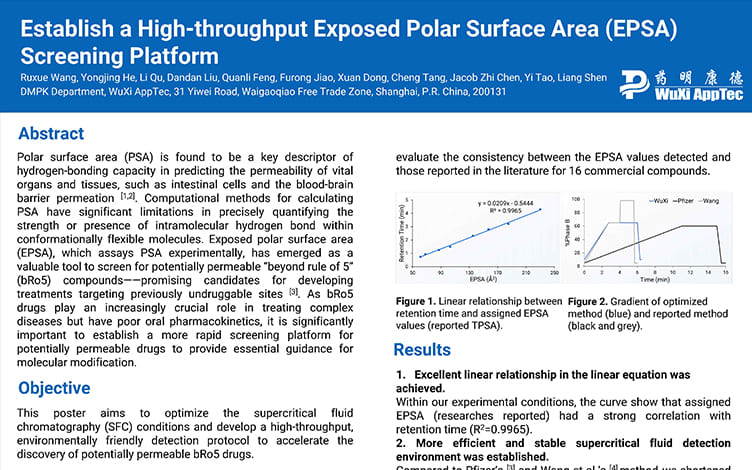
Establish a High-throughput Exposed Polar Surface Area (EPSA) Screening Platform
PostersSep 04, 2025Learn More -


Development of a High-throughput and Cost-effective Method for Experimental Polar Surface Area Measurement with Ultra-Performance Convergence Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
PostersJul 24, 2025Learn More -


Enhancing Permeability Through Exposed Polar Surface Area (EPSA) for Beyond Rule of Five (bRo5) Drug Candidates
ArticlesApr 10, 2025Learn More -


Rapid Determination of Lipophilicity: Exploration and Establishment of Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RPLC) Methods
PostersNov 05, 2024Learn More -


Ensuring drug product integrity: The crucial role of stability testing
BlogsOct 27, 2024Learn More -


How to Evaluate Lipophilicity Rapidly? The Significance of Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
BlogsDec 19, 2023Learn More -


Rapid Determination of Lipophilicity: Establishment and Application of Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
ArticlesNov 30, 2023Learn More -


Focusing on PROTAC Permeability and Solubility Improving the Oral Availability
BlogsJul 07, 2023Learn More -


Research on PROTAC Druggability: Solubility and Permeability
ArticlesJun 30, 2023Learn More
Stay Connected
Keep up with the latest news and insights.