-
Overview
-
Methods
-
Case Study
-
FAQs
-
Related Resources
-
Related Services
Overview
Solubility of compounds has received considerable attention in drug discovery, because it not only plays a key role in gastrointestinal absorption of drugs, oral bioavailability, accurate in vitro bioassays, and selection of appropriate dosage forms for in vivo experiments, but also is one of the important parameters in the establishment of biopharmaceutical BCS classification system. During drug discovery, compounds with insufficient solubility often appear. The issue of insufficient solubility of compounds can be solved by using new solvent formulations or delivery systems. However, this can lead to increased development costs and cycle delays and does not guarantee the druggability of the compounds. If the only candidate compound for development has low solubility, thus, early solubility analysis can at least be provided as an early warning for difficulties.
Different types of solubility data are required to characterize compound properties in different research and development stages. In the early stage of research and development, kinetic solubility is one of the important methods for compound sequencing due to the large number of screening assays and the small amount of compound. As compounds enter the later stage, different crystal forms are usually selected for the study, and the thermodynamic solubility test is a commonly used method in this stage. WuXi AppTec DMPK provides two high-throughput screening methods for solubility measurement.
Learn More



Methods
-
Theoretical Concentration
200 μM(routine)
Media
Aqueous buffer system; Biorelevant media.
Percentage of DMSO
2%(routine); Other ratios, e.g., 1%
Incubation Equilibration Time
24 h (routine); Other time points, e.g., 2 h
Equilibration Temperature
Room temperature or 37 ℃
Compound Required
30 μL of 10 mM DMSO stock solution
Analytical Method
HPLC-UV/HPLC-ELSD/LC-MS/MS
Turnaround Time
3-5 working days
-
Sample Amount
2 mg solid (for solubility assay) and 1 mg solid (for standard curve preparation)
Media
Aqueous buffer system; Biorelevant media; Organic solvent
Incubation Equilibration Time
24 h
Equilibration Temperature
Room temperature or 37 ℃
Analytical Method
HPLC-UV/HPLC-ELSD/LC-MS/MS
Turnaround Time
3-5 working days
Case Study
-
-


Solubility verification data for some commercial reagents
Solubility measurement requires well-developed methods. The Classic Shake-Flask method is employed to obtain the kinetic and thermodynamic solubility of the compounds quickly and accurately. Part of the verification data for some commercial reagents (Condition: phosphate buffer at pH 7.4, RT, 24 h) are shown on the left.
-
FAQs
-
What are the criteria and classifications for solubility acceptance in new drug development?
It really depends on two other factors for the drug: permeability and dose. The more potent (i.e., dose producing the pharmacological effect) and the more permeable of the compound, the lower requirement of the solubility achieve complete absorption. Moreover, the less potent and the less permeable of the compound, the higher requirement of the solubility to achieve complete absorption.
In rating the solubility of compounds for discovery project teams, the following solubility classification ranges are recommended for medicinal chemists:
<10 μg/mL Low solubility
10-60 μg/mL Moderate solubility
>60 μg/mL High solubility
-
How can the reliability of the experiment be ensured?
Three positive controls are used in each type of experiment, which have been verified and have a reference range to ensure the accuracy and consistency of the experimental operation.
-
How do we deal with non-specific adsorption of compounds?
Low-bonding consumables are used in the whole process: 96-well low-bonding filter plates or regenerated cellulose filter membrane syringeless device are used by default for kinetic solubility and thermodynamic solubility assays with potential related problems;
When the sample is treated, it will use additional adsorbent, such as organic solvents, surfactants, proteins, etc., or adjust the pH and other methods to optimize the sample treatment process to minimize the adsorption.
-
When the solubility of a compound is very low, how do you ensure that the specific solubility value is detected?
HPLC-UV method is preferred for analysis, and the lower limit of quantification is set at about 1 μM. If the solubility value of the compound is very low, but you still want to measure the specific value, you can try to use LC-MS/MS analysis, and the conventional lower limit of quantification is set at about 1 nM. And it can be adjusted as needed.
-
If the compound has stability problems, can it be found and how to deal with them?
The solubility test is preferentially analyzed by chromatography and full-wavelength scanning to find out whether there is a specific degradation peak.
LC-UV-MS in series can be used to determine the target peak.
For some special cases, it needs to further assess the unstable factors and optimize the experimental conditions.
Related Resources




-


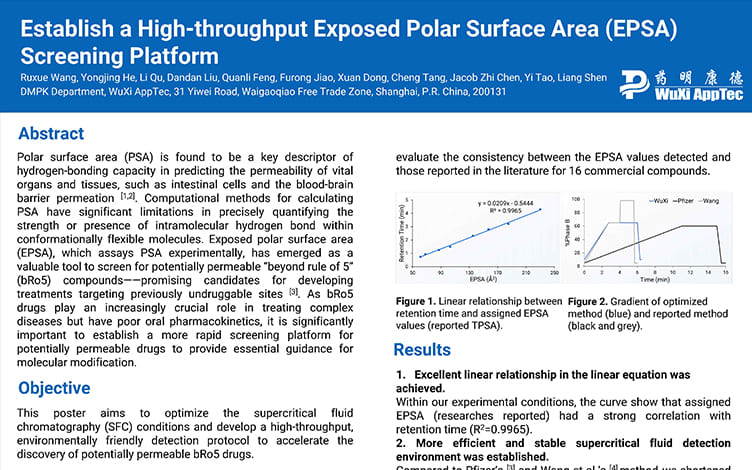
Establish a High-throughput Exposed Polar Surface Area (EPSA) Screening Platform
PostersSep 04, 2025Learn More -


Development of a High-throughput and Cost-effective Method for Experimental Polar Surface Area Measurement with Ultra-Performance Convergence Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
PostersJul 24, 2025Learn More -


Enhancing Permeability Through Exposed Polar Surface Area (EPSA) for Beyond Rule of Five (bRo5) Drug Candidates
ArticlesApr 10, 2025Learn More -


Rapid Determination of Lipophilicity: Exploration and Establishment of Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RPLC) Methods
PostersNov 05, 2024Learn More -


Ensuring drug product integrity: The crucial role of stability testing
BlogsOct 27, 2024Learn More -


How to Evaluate Lipophilicity Rapidly? The Significance of Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
BlogsDec 19, 2023Learn More -


Rapid Determination of Lipophilicity: Establishment and Application of Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
ArticlesNov 30, 2023Learn More -


Focusing on PROTAC Permeability and Solubility Improving the Oral Availability
BlogsJul 07, 2023Learn More -


Research on PROTAC Druggability: Solubility and Permeability
ArticlesJun 30, 2023Learn More
Stay Connected
Keep up with the latest news and insights.